Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2013; 5(3): 50-59
Published online Mar 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i3.50
Published online Mar 15, 2013. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v5.i3.50
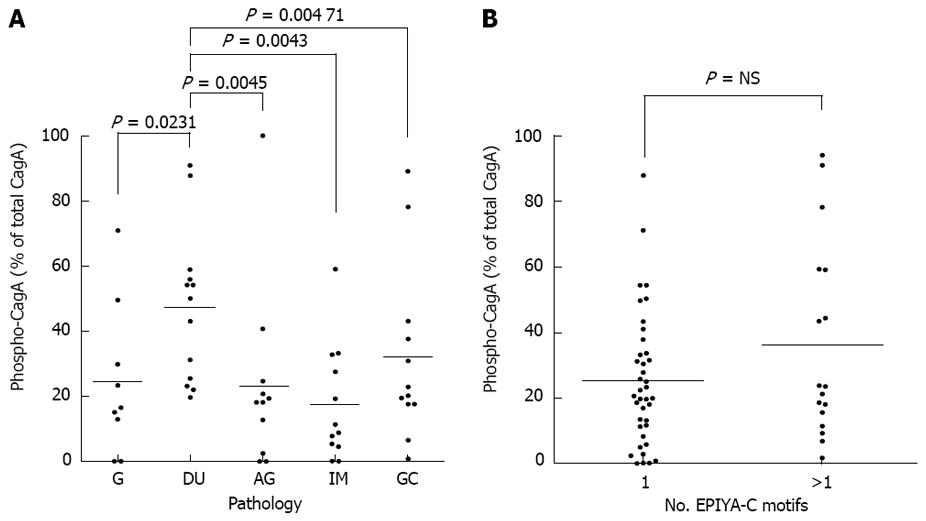
Figure 3 CagA-protein phosphorylation and its relationship to Glu-Pro-Ile-Tyr-Ala-C (EPIYA-C) motifs and disease severity.
Sixty functional-cagPAI strains were cocultured with AGS cells for 6 h. Coculture lysates were assessed by Western blot and levels of CagA phosphorylation were determined by densitometry. A: Evaluation of CagA phosphorylation levels according to the pathology from which strains were isolated; B: Relationship between the number of EPIYA motifs and the levels of CagA phosphorylation. G: Gastritis; DU: Duodenal ulcer; AG: Atrophic gastritis; IM: Intestinal metaplasia; GC: Gastric cancer. NS: Not significant
-
Citation: Fajardo CA, Quiroga AJ, Coronado A, Labrador K, Acosta N, Delgado P, Jaramillo C, Bravo MM. CagA EPIYA polymorphisms in Colombian
Helicobacter pylori strains and their influence on disease-associated cellular responses. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2013; 5(3): 50-59 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v5/i3/50.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v5.i3.50