Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2012; 4(12): 238-249
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238
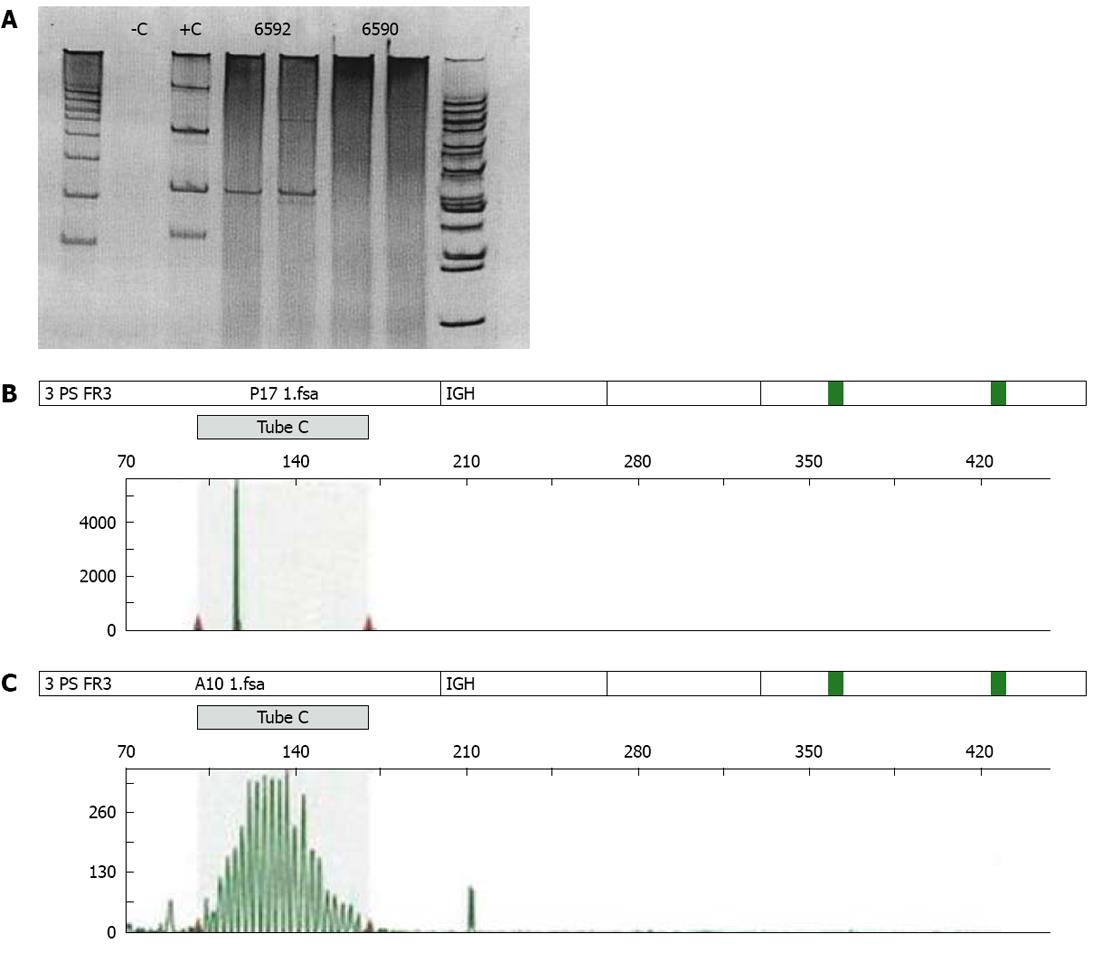
Figure 4 Polymerase chain reaction.
A: Polyclonal B-cell pathology results in a broad smear of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product on a gel, while a monoclonal pathology (lymphoma) will give rise to a sharp band on a gel, hereby reflecting PCR products that have the same size. +C: Positive control; -C: Negative control; 6592: Tumor case; 6590: Reactive case; B: Gaussian curve in a polyclonal B-cell population examined by multiplex PCR; C: Peak in a neoplastic B-cell clone examined by multiplex PCR.
- Citation: Sagaert X, Tousseyn T, Yantiss RK. Gastrointestinal B-cell lymphomas: From understanding B-cell physiology to classification and molecular pathology. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2012; 4(12): 238-249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v4/i12/238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238