Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2012; 4(12): 238-249
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238
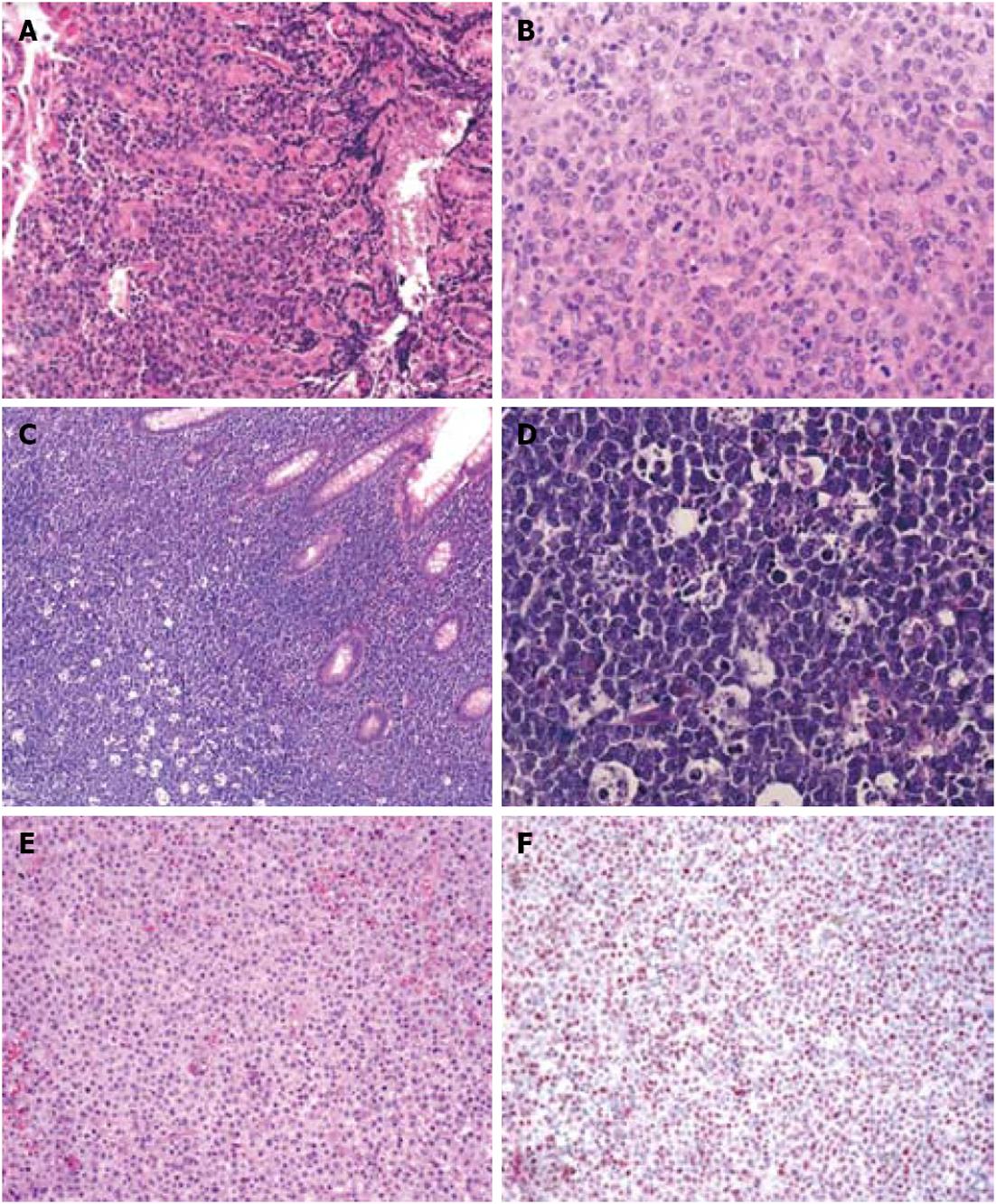
Figure 3 Histology of other gastrointestinal B-cell lymphomas.
A: Hematoxylin eosin (HE) staining of a gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (magnification 200 ×); B: Polymorphic appearance of the large tumor B-cells in a gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (magnification 400 ×); C: HE staining of an intestinal Burkitt lymphoma with the typical “starry sky” appearance (magnification 100 ×); D: Presence of multiple pale macrophages filled with apoptotic debris in an intestinal Burkitt lymphoma (magnification 400 ×); E: HE staining of an intestinal monomorphic post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD) (magnification 200 ×); F: In situ hybridization demonstrates presence of EBV-encoded RNA (= red colored nuclei) in the neoplastic cells of an intestinal monomorphic PTLD (magnification 100 ×).
- Citation: Sagaert X, Tousseyn T, Yantiss RK. Gastrointestinal B-cell lymphomas: From understanding B-cell physiology to classification and molecular pathology. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2012; 4(12): 238-249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v4/i12/238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238