Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 104922
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.104922
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.104922
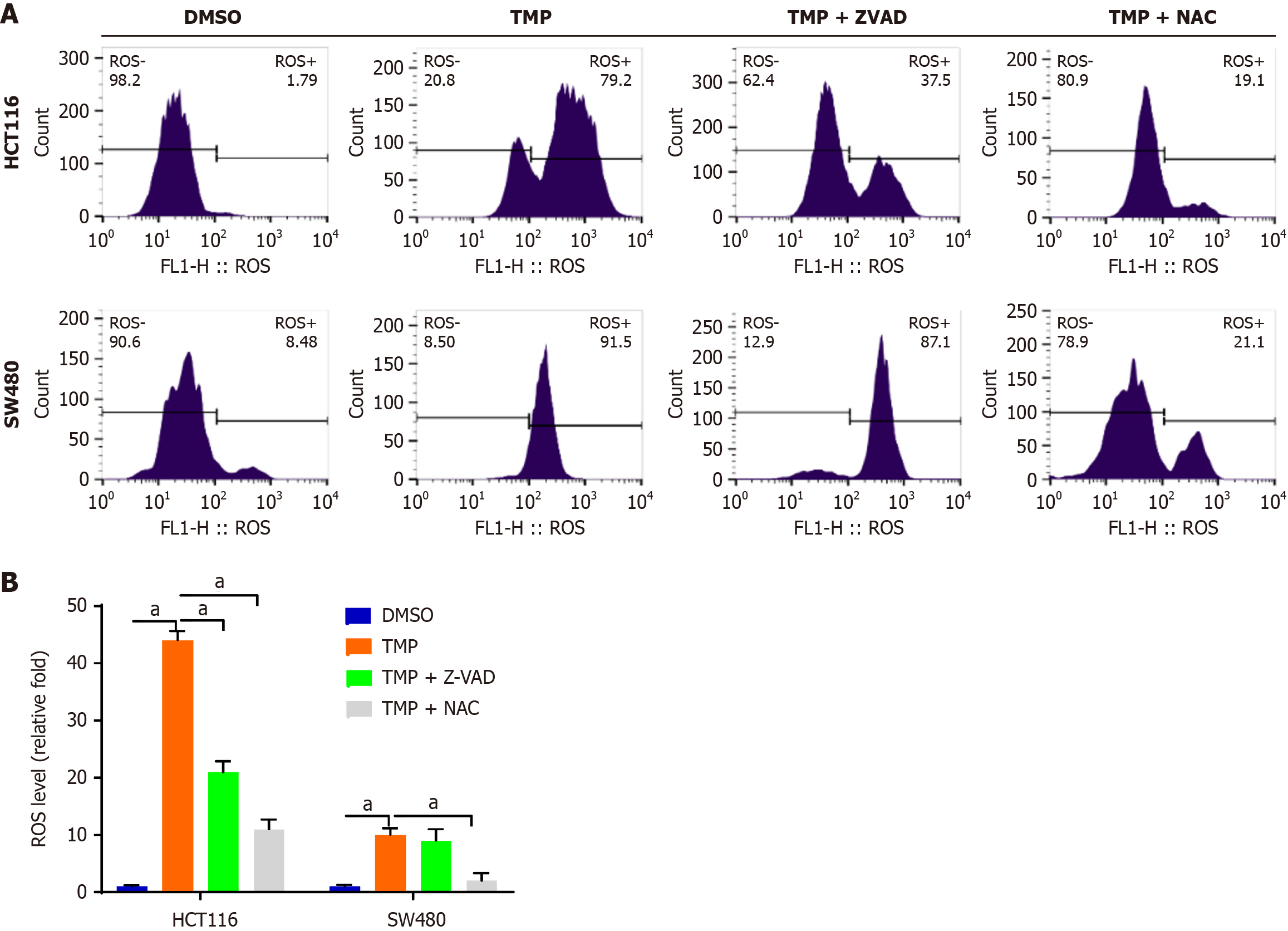
Figure 2 N-acetyl-L-cysteine and Z-VAD-FMK inhibit tetramethylpyrazine-induced accumulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species.
A: Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) of SW480 and HCT116 cells treated with tetramethylpyrazine with or without Z-VAD-FMK and N-acetyl-L-cysteine detected by flow cytometry; B: Bar chart of intracellular ROS level in four groups of SW480 and HCT116 cells treated as indicated. aP < 0.001. TMP: Tetramethylpyrazine; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine.
- Citation: Hou YX, Ren W, He QQ, Huang LY, Gao TH, Li H. Tetramethylpyrazine induces reactive oxygen species-based mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in colon cancer cells. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 104922
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/104922.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.104922