Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 103591
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103591
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103591
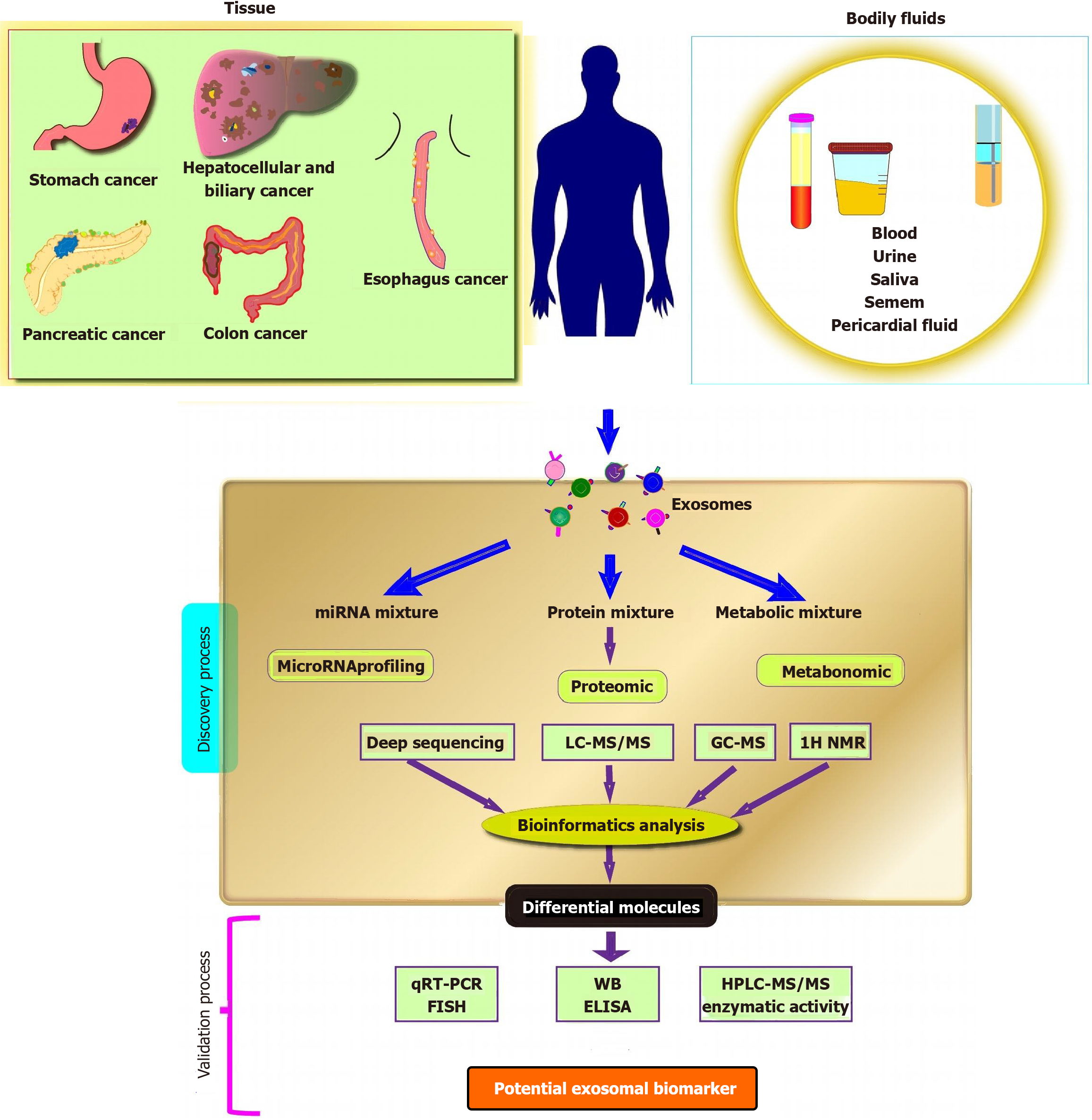
Figure 3 Clinical application of exosomal biomarkers for gastrointestinal diagnostic.
Biopsies of exosomes include tumor tissue, blood, urine, saliva and feces. These sources contain cancer-derived exosome-encapsulated microRNAs, proteins and metabolic molecules. Treatment efficacy is monitored in real time by detecting and quantifying these molecular targets in association with tumor stage. miRNA: MicroRNA; LC-MS/MS: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; GC-MS: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; qRT-PCR: Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridization; WB: Western blot; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HPLC-MS/MS: High performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Yue NN, Chen LY, Tian CM, Yao J, Wang LS, Liang YJ, Wei DR, Ma HL, Li DF. Exosomal biomarkers: A novel frontier in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 103591
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/103591.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.103591