Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 100497
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.100497
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.100497
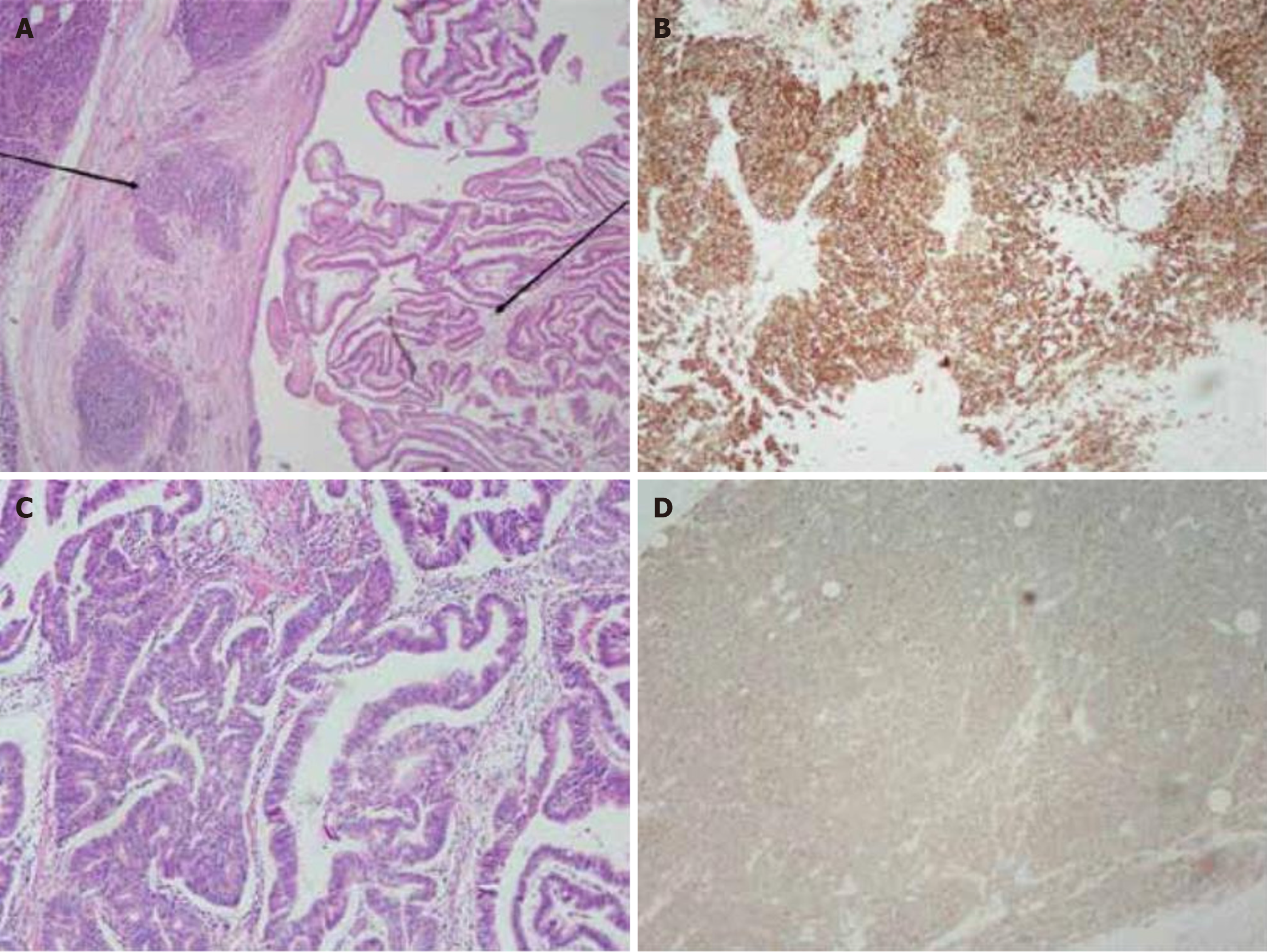
Figure 3 Pathological sections of the specimen.
A: Pathological specimen showing pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinomas (small cell neuroendocrine carcinomas) on the left and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile duct on the right [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, 100 ×]; B: Immu
- Citation: Yi AQ, Xie GH. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms coexisting with biliary intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 100497
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/100497.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.100497