Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2025; 17(4): 100497
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.100497
Published online Apr 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.100497
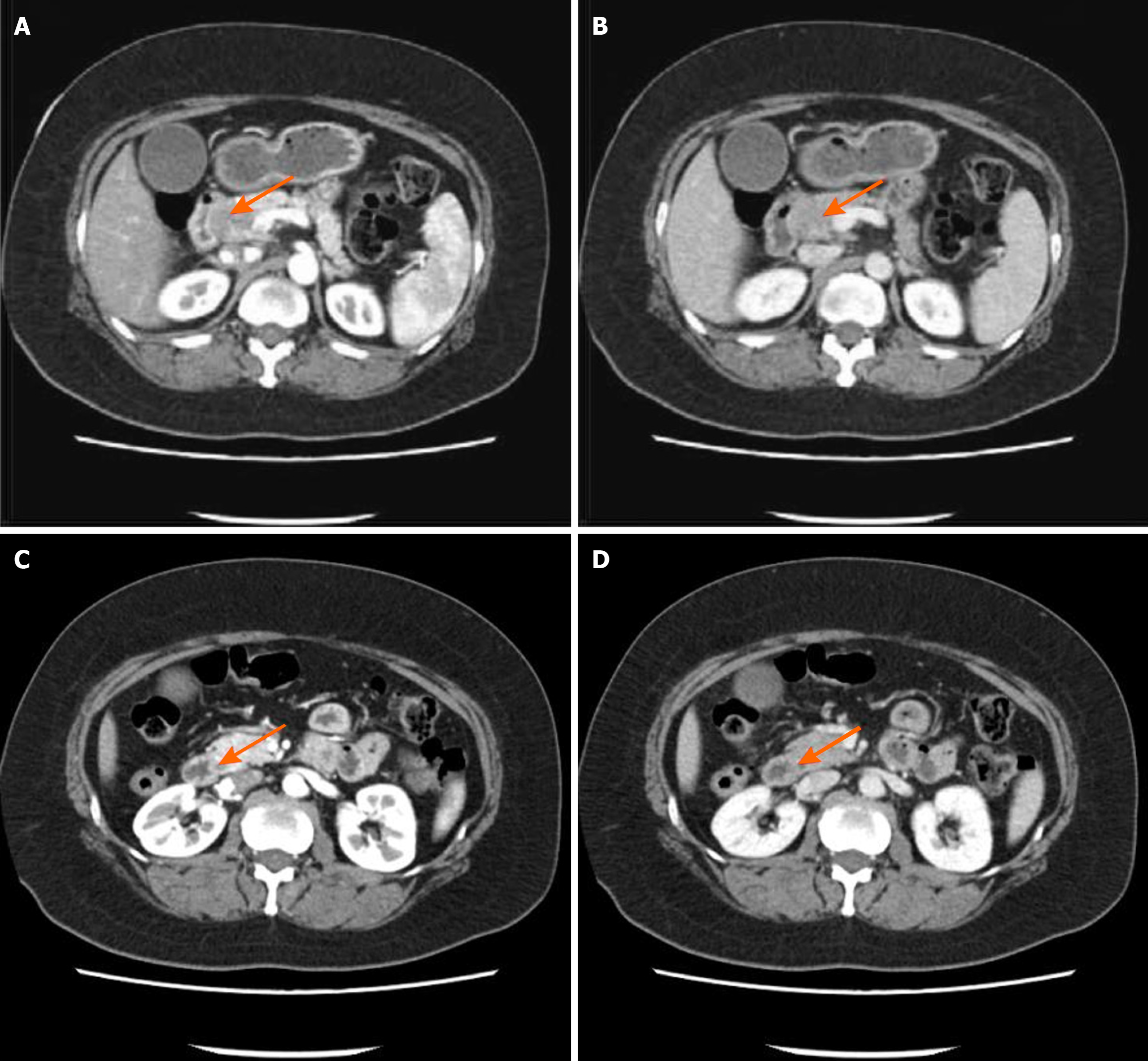
Figure 1 Upper abdominal enhanced computed tomography images.
A: The pancreatic head in the arterial phase of upper abdominal enhanced computed tomography (CT); B: The pancreatic head in the venous phase of upper abdominal enhanced CT; C: The pancreatic duct in the upper segment in the arterial phase of upper abdominal enhanced CT; D: The pancreatic duct in the upper segment in the venous phase of upper abdominal enhanced CT. The imaging examinations were performed using a 64-row multidetector CT scanner with scan parameters of 120 kV, 200 mA, slice thickness of 5 mm, and an interval of 5 mm. The patient received an intravenous contrast agent (iodinated contrast agent, 1.5 mL/kg), and the scan duration was 25 seconds for the arterial phase and 70 seconds for the venous phase. The imaging data were independently analyzed by two radiologists with extensive clinical experience, and the conclusions were reached through a consensus assessment.
- Citation: Yi AQ, Xie GH. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms coexisting with biliary intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(4): 100497
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i4/100497.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.100497