Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 98844
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.98844
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.98844
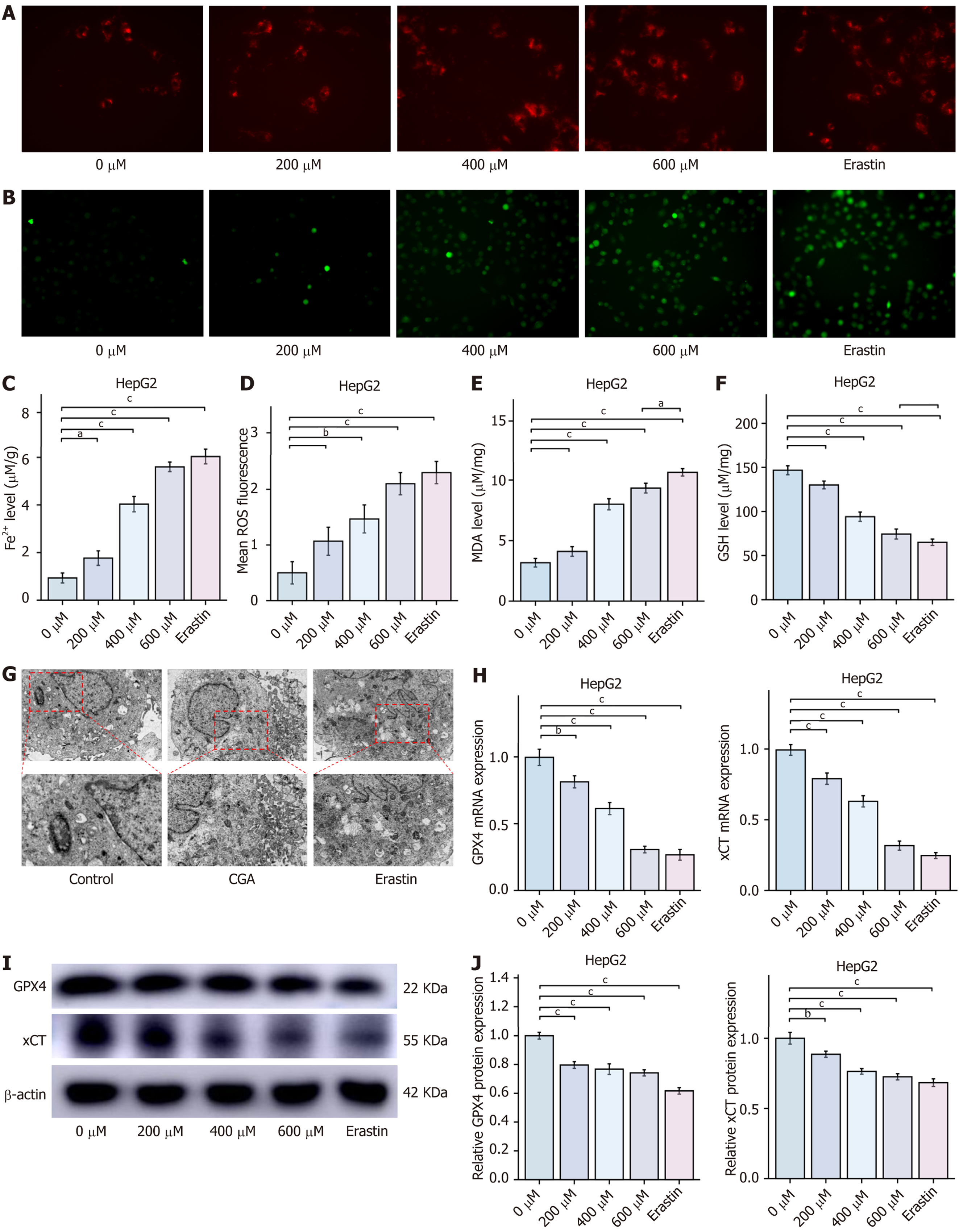
Figure 6 Chlorogenic acid induces ferroptosis in HepG2 cells (mean ± SD, n = 3).
A: Intracellular Fe2+levels; B: Intracellular reactive oxygen species levels detected by BODIPY 581/591 C11 lipid peroxidation probe; C: Statistics of intracellular Fe2+levels; D: Statistics of intracellular reactive oxygen species levels; E: Malondialdehyde levels; F: Glutathione levels; G: TEM images of mitochondrial ultrastructure; H: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of cystine glutamate reverse transporter and glutathione peroxidase 4 mRNA expression in HepG2 cells; I and J: Western blot analysis of cystine glutamate reverse transporter and glutathione peroxidase 4 protein expression in HepG2 cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and cP < 0.001 compared to the 0 μmol chlorogenic acid group. ROS: Reactive oxygen species; MDA: Malondialdehyde; GSH: Glutathione; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; xCT: Cystine glutamate reverse transporter.
- Citation: Wu L, Chen HY, Zhang JT, Yang RY, Wang ZB, Xue PS, Peng W, Li KX, Gao WH, Zeng PH. Chlorogenic acid induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell ferroptosis via PTGS2/AKR1C3/GPX4 axis-mediated reprogramming of arachidonic acid metabolism. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 98844
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/98844.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.98844