Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 98844
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.98844
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.98844
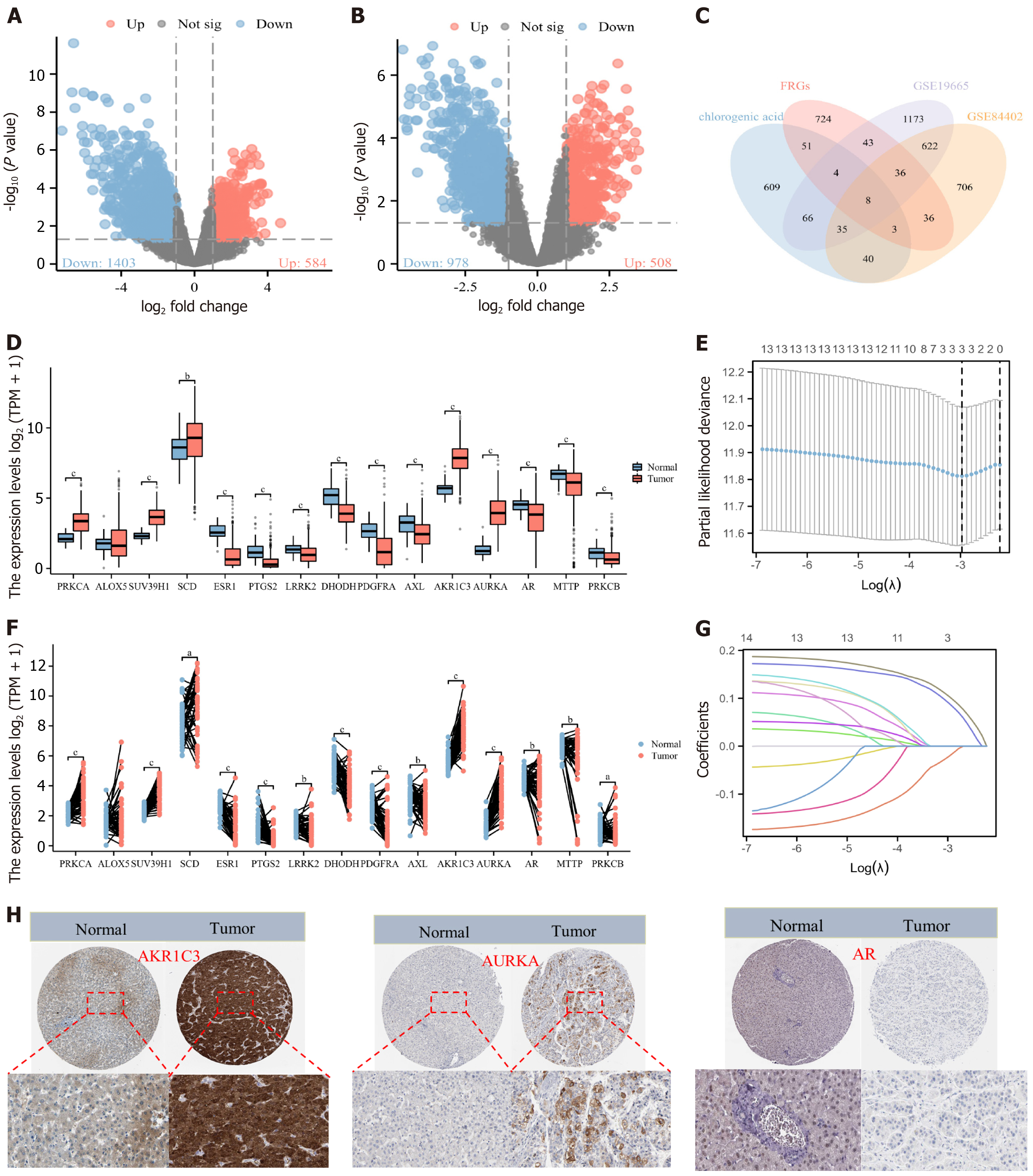
Figure 3 Acquisition, expression difference, and prognostic analysis of chlorogenic acid intervention targets (mean ± SD, n = 374).
A: Volcano plot of differential analysis based on GSE19665 dataset; B: Volcano plot of differential analysis based on GSE84402 dataset; C: Venn diagram showing the intersection of chlorogenic acid (CGA) targets, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) targets from GSE19665 and GSE84402 datasets, and ferroptosis-related genes; D: Unpaired expression analysis of CGA intervention targets in HCC patients; F: Paired expression analysis of CGA intervention targets in HCC patients; E and G: Lasso regression analysis of CGA intervention targets; H: Immunohistochemical analysis of CGA intervention targets in the Human Protein Atlas database. Not sig: Not significant; FRG: Ferroptosis-related genes; TPM: Transcripts per million; AKR1C3: Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3; AURKA: Aurora kinase A; AR: Androgen receptor.
- Citation: Wu L, Chen HY, Zhang JT, Yang RY, Wang ZB, Xue PS, Peng W, Li KX, Gao WH, Zeng PH. Chlorogenic acid induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell ferroptosis via PTGS2/AKR1C3/GPX4 axis-mediated reprogramming of arachidonic acid metabolism. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 98844
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/98844.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.98844