Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 103450
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450
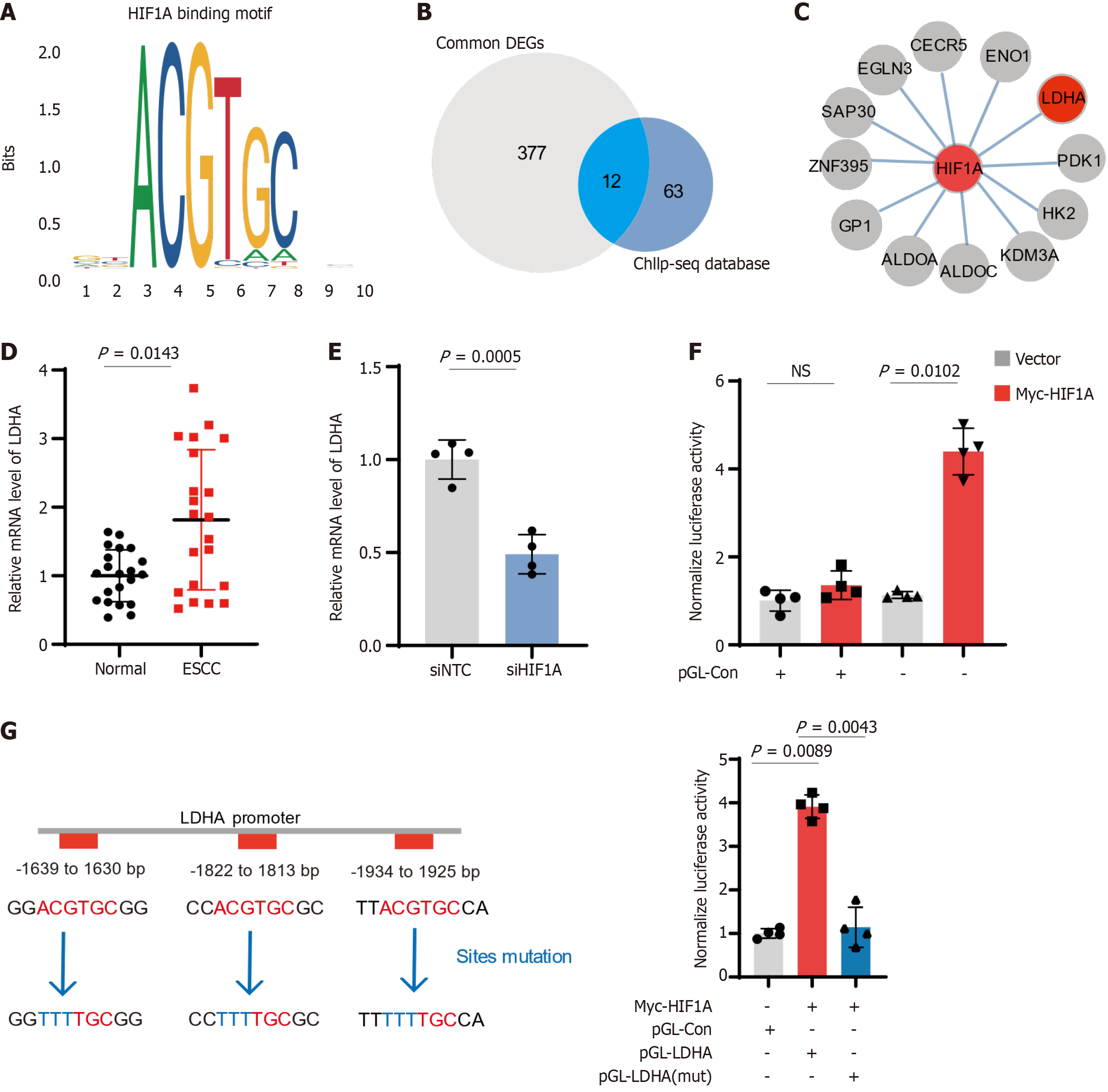
Figure 4 Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha-mediated regulation of lactate dehydrogenase A expression in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma.
A: Representation predicted binding motif of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A); B: Venn diagram showing overlap between differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC) and genes identified in the ChIP-seq database for HIF1A binding sites. A total of 12 common genes are highlighted; C: Interaction network of HIF1A with common DEGs and key metabolic enzymes in ESCC; D: Relative mRNA levels of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) in 21 paired ESCC patient tissues; E: LDHA mRNA levels decrease significantly upon HIF1A knockdown in ESCC cells; F: Luciferase assay demonstrating the transcriptional activity of LDHA promoter; G: Analysis of LDHA promoter mutations affecting HIF1A binding. ESCC: Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma; LDHA: Lactate dehydrogenase A; HIF1A: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; siNTC: Non-targeting control siRNA; siHIF1A: HIF1A-targeting siRNA.
- Citation: Chen X, Liu HY, Zhou WB, Zhang LL, Huang J, Bao DW. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and lactate dehydrogenase-A axis in metabolic changes and aggression in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 103450
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/103450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450