Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 103450
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450
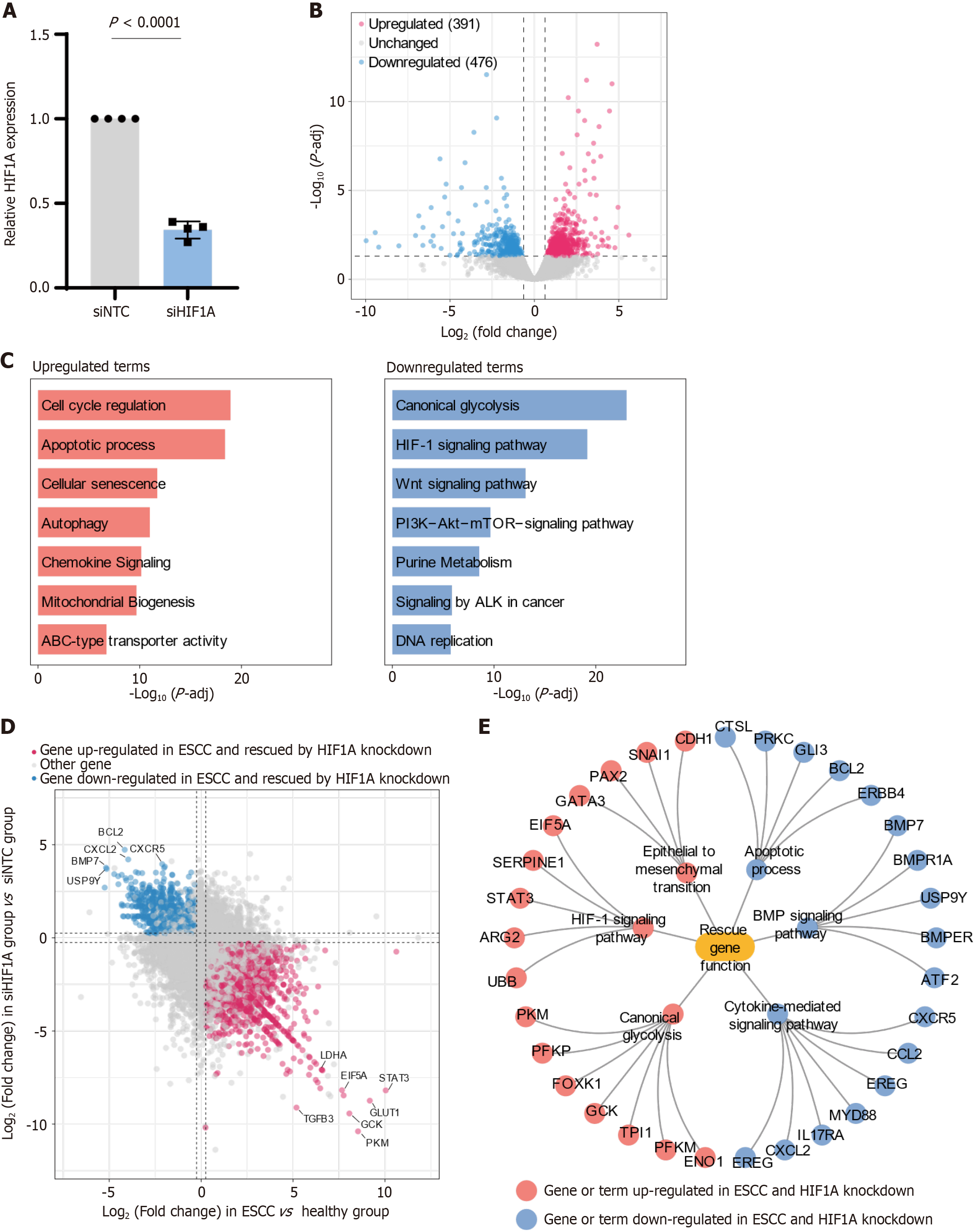
Figure 3 Analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha knockdown effects on gene expression and pathway modulation in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma.
A: The relative mRNA expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A) in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells treated with non-targeting control siRNA (siNTC) and HIF1A-targeting siRNA (siHIF1A); B: Volcano plot illustrating differential gene expression in ESCC cells following HIF1A knockdown. The plot identifies 391 upregulated genes (red dots) and 476 downregulated genes (blue dots), while unchanged genes are shown in gray. The plot highlights the extensive impact of HIF1A knockdown on the cellular transcriptome; C: Bar graphs showing enriched biological pathways among genes differentially expressed after HIF1A knockdown. The top upregulated pathways include cell cycle regulation, apoptotic processes, and cellular senescence, suggesting a shift towards reduced proliferation and enhanced cell death. Conversely, the most significant downregulated pathways are canonical glycolysis, HIF-1 signaling, and Wnt signaling, indicating a decrease in metabolic adaptation and signaling processes critical for tumor progression; D: Scatter plot comparing gene expression changes in ESCC vs healthy tissues (x-axis) with those in siHIF1A vs siNTC cells (y-axis). Genes upregulated in ESCC and downregulated after HIF1A knockdown (red) and genes downregulated in ESCC and upregulated after knockdown (blue) are highlighted, indicating "rescue" of these genes by HIF1A inhibition; E: Network diagram representing the functional implications of genes rescued by HIF1A knockdown. The diagram includes key pathways and processes such as epithelial to mesenchymal transition, apoptotic processes, and Bone Morphogenetic Protein signaling, with connections indicating how the suppression of HIF1A influences these pathways, potentially reversing key aspects of tumor metastasis and progression. Nodes represent genes or terms that were upregulated (red) or downregulated (blue) in ESCC and reversed by HIF1A knockdown.
- Citation: Chen X, Liu HY, Zhou WB, Zhang LL, Huang J, Bao DW. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and lactate dehydrogenase-A axis in metabolic changes and aggression in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 103450
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/103450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450