Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 102187
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.102187
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.102187
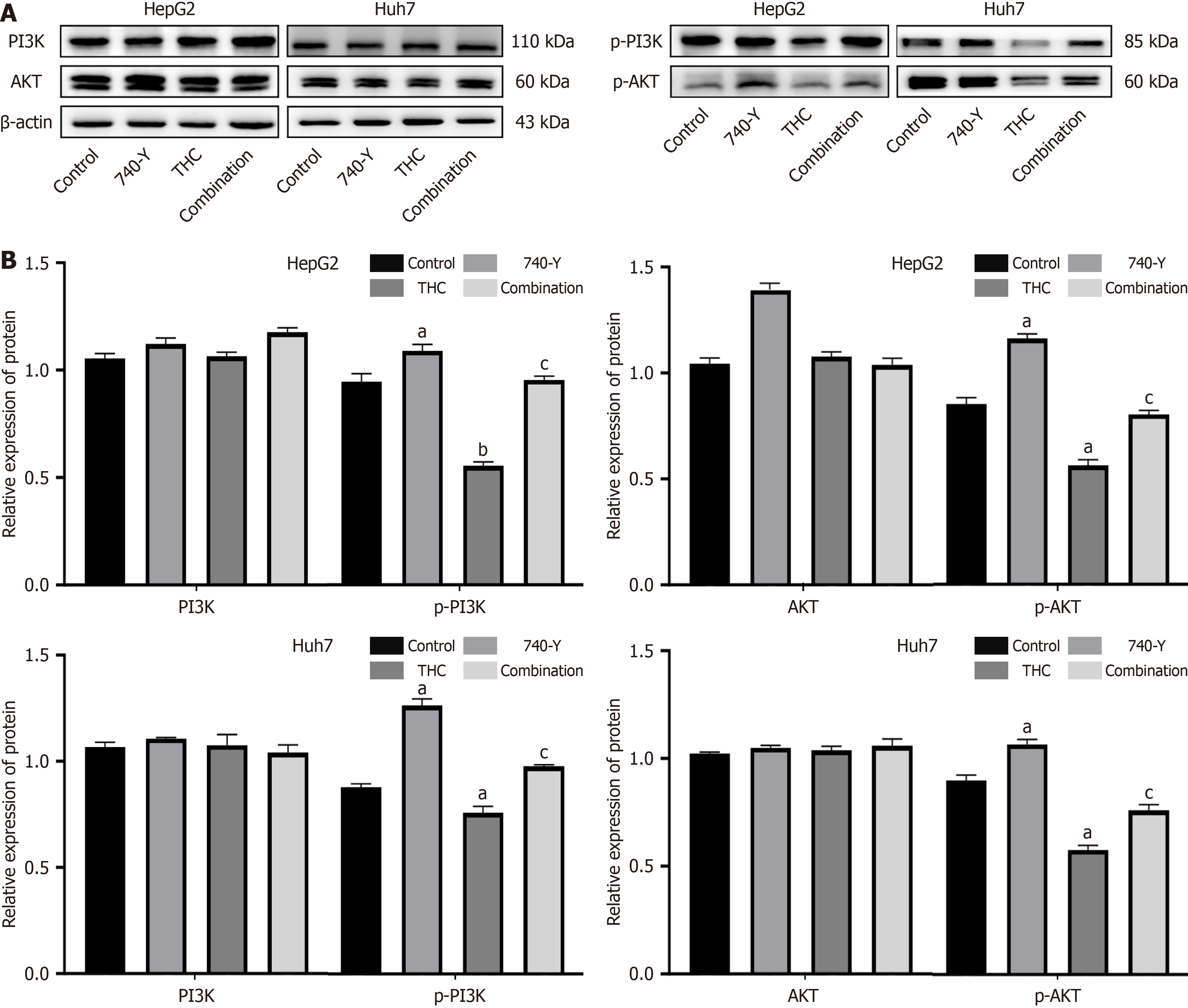
Figure 12 Signaling pathway agonist treatment to validate the effects of curcumin on phosphoinositide 3-kinases/AKT core protein levels.
A: Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) inhibits the phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/AKT pathway in HepG2 and Huh7 liver cancer cells. HepG2 and Huh7 cells were treated with 0 μM THC, PI3K activator 740 Y-P, THC (50 μM), or a combination of THC (50 μM) and 740 Y-P for 48 hours. The protein expression of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, and p-AKT was analyzed using western blot analysis. Representative bands of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, and p-AKT protein expression in HepG2 and Huh7 cells after different treatments are shown in graph; B: The protein expression levels of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, and p-AKT in HepG2 and Huh7 cells after different treatments are illustrated in the bar graph. All data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. aP < 0.05 vs the control group, bP < 0.01 vs the control group, cP < 0.01 vs THC (50 μM). PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinases; THC: Tetrahydrocurcumin.
- Citation: Bao ZC, Liu ZD, Zhang Y, Dai HJ, Jia H, Ren F, Li N, Zhao L, Wang YW, Lv SY, Zhang Y. To investigate the effect and mechanism of tetrahydrocurcumin on hepatocellular carcinoma based on phosphoinositide 3-kinases/AKT signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 102187
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/102187.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.102187