Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 101174
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.101174
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.101174
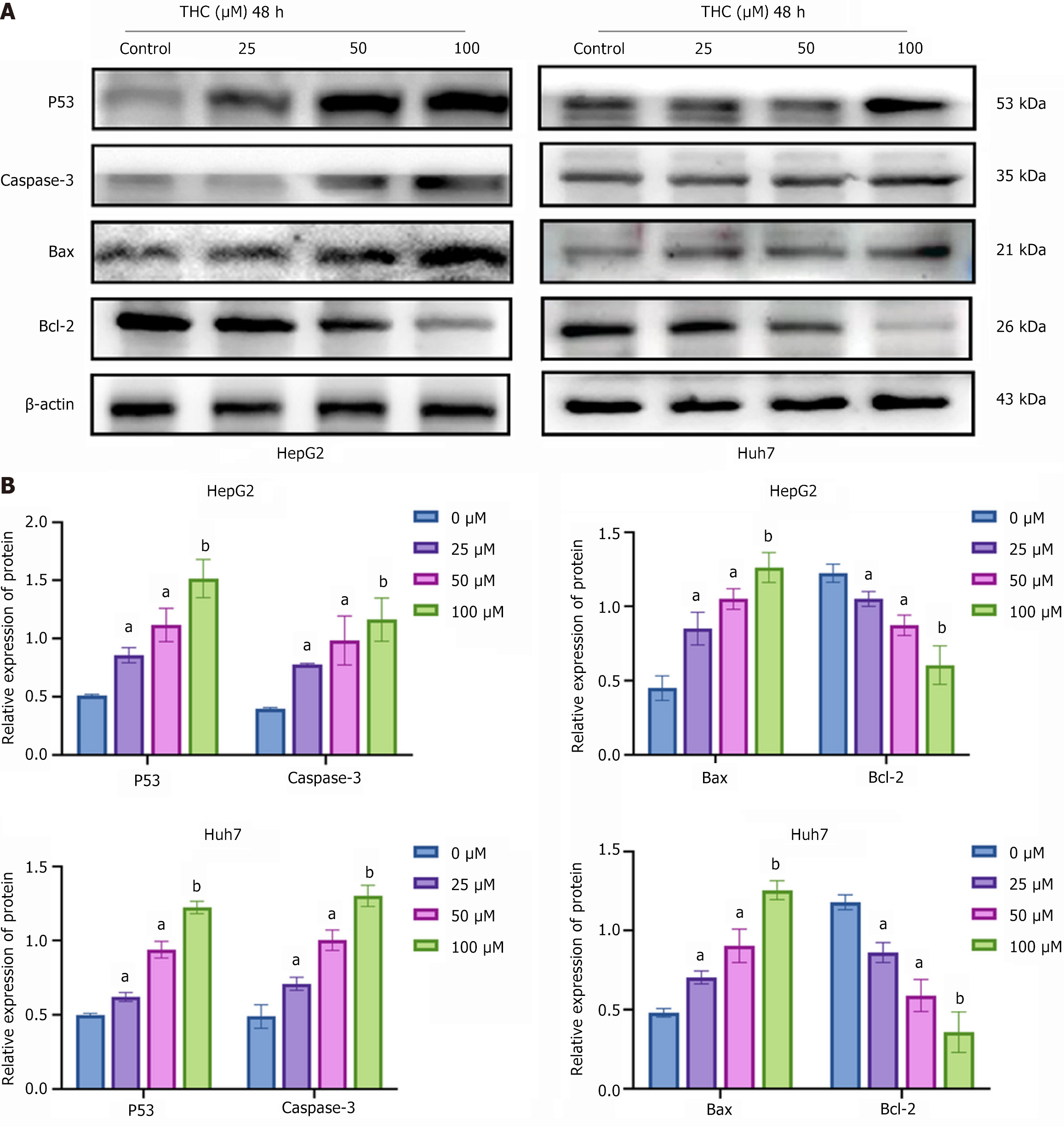
Figure 10 Effect of tetrahydrocurcumin on the expression of P53 signaling pathway-related proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Western blotting analysis of core P53 signaling pathway-related proteins. HepG2 and Huh7 cells were treated with tetrahydrocurcumin (25, 50, or 100 μM) for 48 hours. Representative blots of P53, caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 protein expression; B: Western blotting analysis of the expression of core proteins related to the P53 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells after drug treatment. All data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; THC: Tetrahydrocurcumin.
- Citation: Bao ZC, Zhang Y, Liu ZD, Dai HJ, Ren F, Li N, Lv SY, Zhang Y. Tetrahydrocurcumin-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells involves the TP53 signaling pathway, as determined by network pharmacology. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 101174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/101174.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.101174