Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2025; 17(3): 101174
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.101174
Published online Mar 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.101174
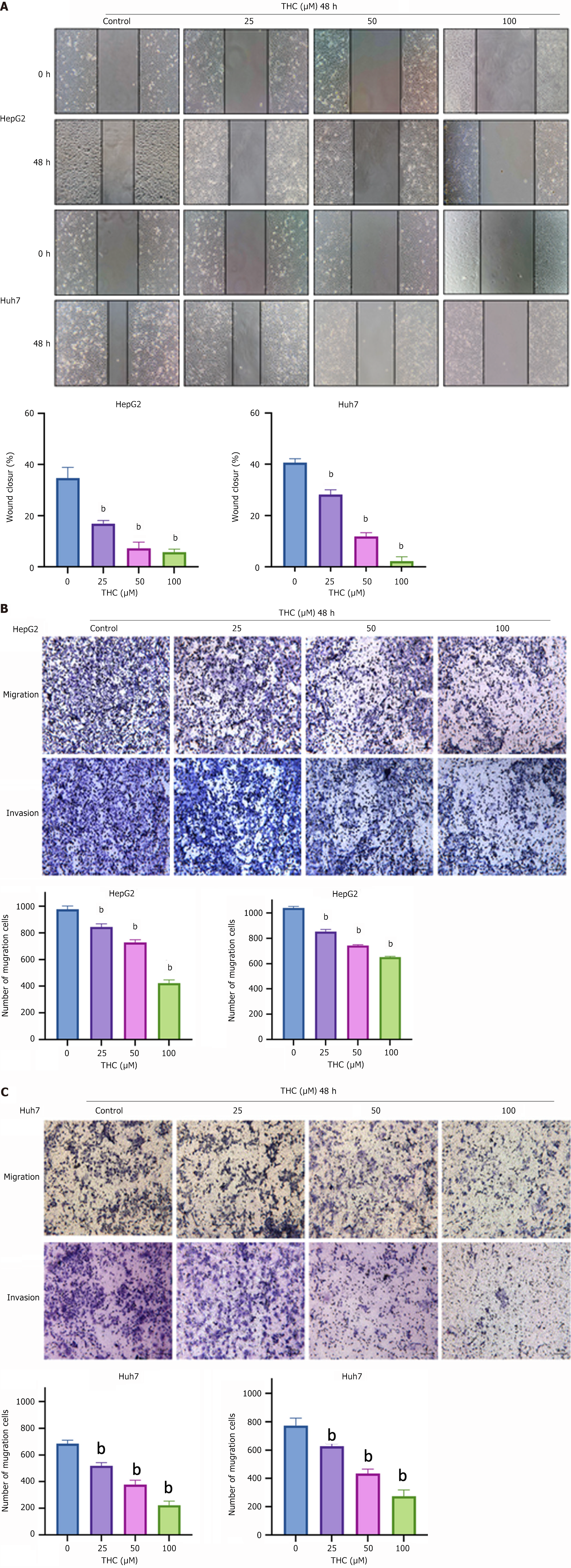
Figure 8 Effect of tetrahydrocurcumin on the migration and invasion of HepG2 and Huh7 cells.
A: The migration capacity of HepG2 cells and Huh7 cells treated with different concentrations of tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) (25, 50, or 100 μmol/L) for 48 hours was detected using a wound-healing assay. All data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3. Compared to the control group, bP < 0.01; B: Transwell assays were conducted to determine the inhibitory effect of different concentrations of THC (25, 50, or 100 μmol/L) on the migration of HepG2 cells. Similarly, matrix glue was used to demonstrate the inhibitory effect of THC on cell invasion, and the number of cells passing through the cell chambers after 48 hours of treatment was statistically analyzed. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 3. Compared to the control group, bP < 0.01; C: Transwell assays were conducted to determine whether THC inhibited the migration of Huh7 cells at different concentrations (25, 50, and 100 μmol/L). Matrix glue was used to determine the inhibitory effect of THC on cell invasion. The number of cells that passed through cell chambers after 48 hours of treatment was statistically analyzed. All data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3. Compared to the control group, bP < 0.01; THC: Tetrahydrocurcumin.
- Citation: Bao ZC, Zhang Y, Liu ZD, Dai HJ, Ren F, Li N, Lv SY, Zhang Y. Tetrahydrocurcumin-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells involves the TP53 signaling pathway, as determined by network pharmacology. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(3): 101174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i3/101174.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.101174