Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 98556
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98556
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98556
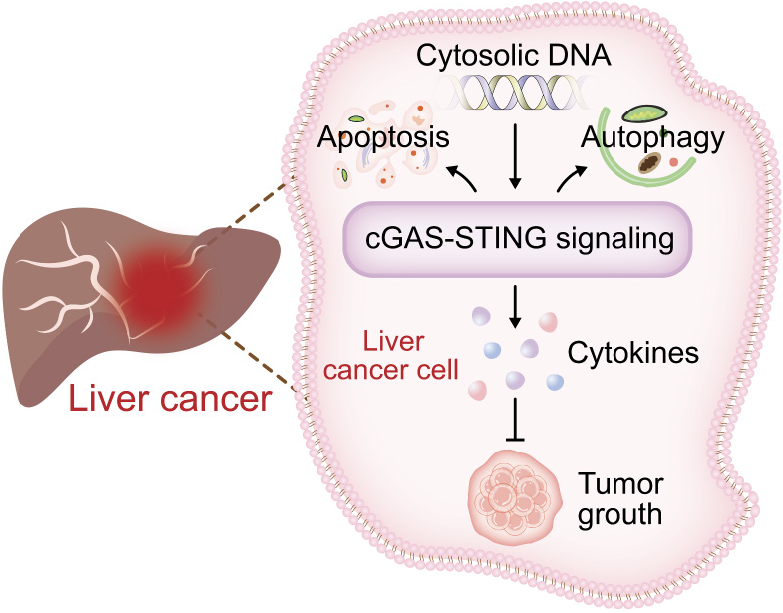
Figure 3 The role of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
The pivotal role of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene (cGAS-STING) signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is profound. When DNA damage occurs within HCC cells, it triggers the formation of double-stranded DNA. This, in turn, stimulates and activates the cGAS-STING signaling cascade, ultimately inducing autophagy and activating the apoptotic process. Furthermore, this pathway facilitates the release of cytokines, which subsequently elicits a robust systemic antitumor immune response. This immune response is instrumental in controlling both local and distant metastasis, thereby mitigating the progression of tumor growth.
- Citation: Nie AY, Xiao ZH, Deng JL, Li N, Hao LY, Li SH, Hu XY. Bidirectional regulation of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon gene pathway and its impact on hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 98556
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/98556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98556