Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 92437
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.92437
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.92437
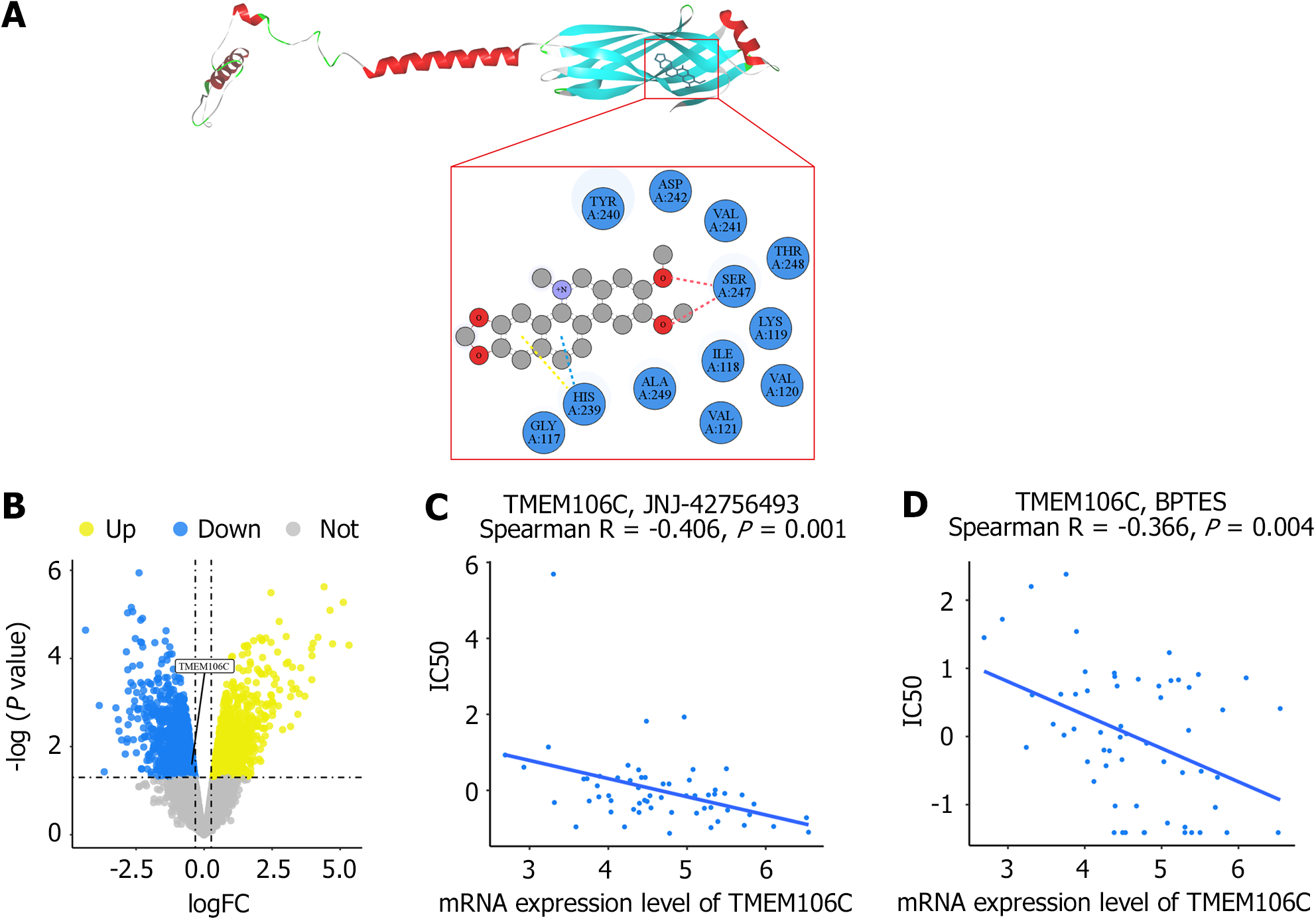
Figure 10 Transmembrane protein 106C as a putative therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: The predicted transmembrane protein 106C (TMEM106C) protein was docked with the nitidine chloride ligand, revealing conventional hydrogen bonds (indicated by red dotted lines), pi-donor hydrogen bonds (indicated by blue dotted lines), and pi-pi T-shaped molecular interactions (indicated by yellow dotted lines); B: Treatment with nitidine chloride down-regulated TMEM106C mRNA expression in a nude mice hepatocellular carcinoma model; C and D: TMEM106C expression level was found to be significantly correlated with drug sensitivity of anti-hepatocellular carcinoma agents, including a multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor, JNJ-42756493 (erdafitinib), and a glutaminase inhibitor, bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl) ethyl sulfide. ALA: Alanine; ASP: Aspartic acid; BPTES: Bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl) ethyl sulfide; GLY: Glycine; HIS: Histidine; IC50: Half-maximal inhibitory concentration; ILE: Isoleucine; LYS: Lysine; SER: Serine; THR: Threonine; TMEM106C: Transmembrane protein 106C; TYR: Tyrosine; VAL: Valine.
- Citation: Li JD, He RQ, Dang YW, Huang ZG, Xiong DD, Zhang L, Du XF, Chen G. Unveiling expression patterns, mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities of transmembrane protein 106C: From pan-cancers to hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 92437
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/92437.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.92437