Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 92437
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.92437
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.92437
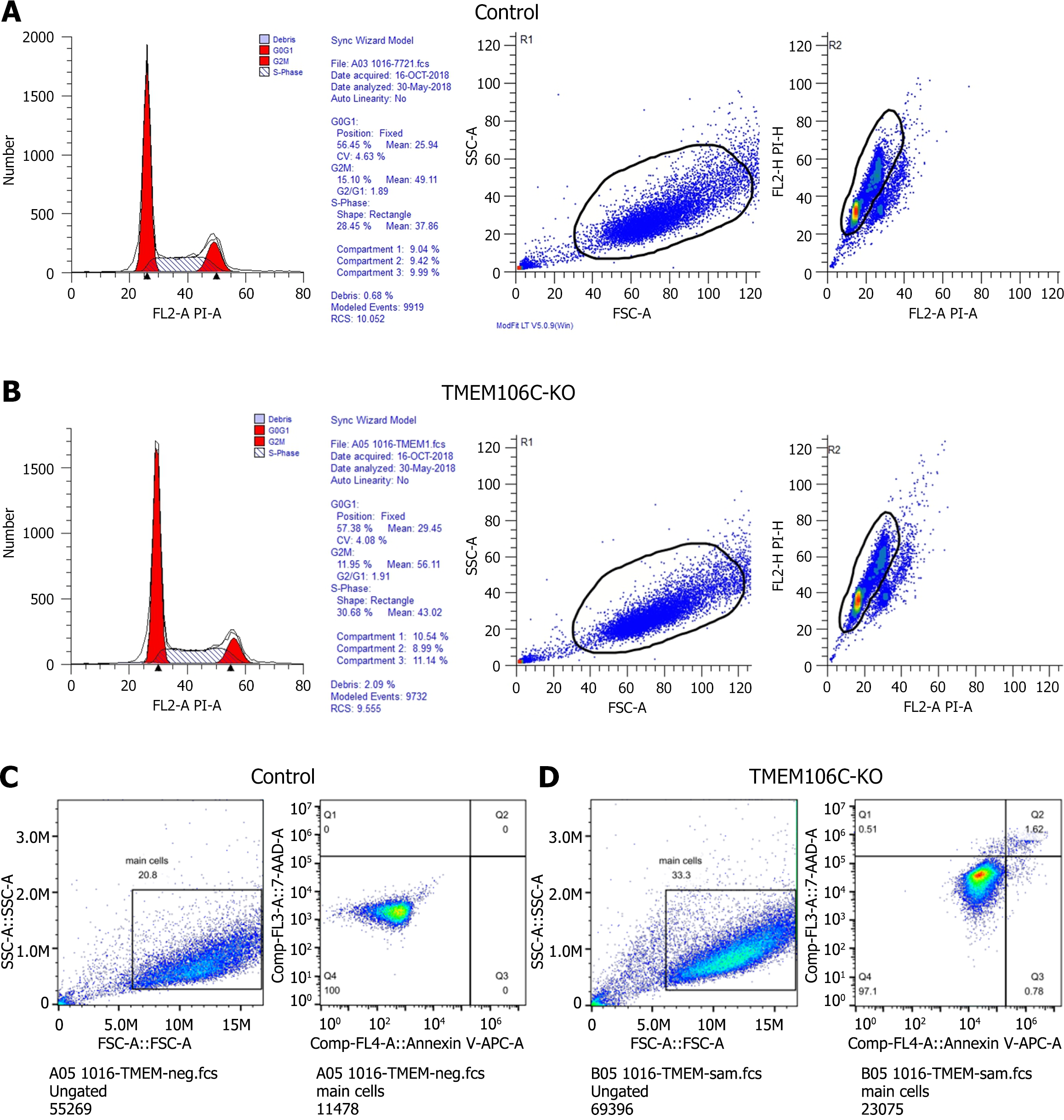
Figure 6 Biological functions of transmembrane protein 106C in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A and B: Transmembrane protein 106C (TMEM106C) knockout arrested the cell cycle process during the DNA synthesis phase; C and D: TMEM106C knockout increased both early and late apoptotic rates of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FL2-A: The area under the curve of the fluorescence signal detected in the FL2 channel; KO: Knockout; PI-A: The area under the curve of the fluorescence signal detected by the flow cytometer after propidium iodide staining; SSC-A: The area under the curve of the side scatter signal; TMEM106C: Transmembrane protein 106C.
- Citation: Li JD, He RQ, Dang YW, Huang ZG, Xiong DD, Zhang L, Du XF, Chen G. Unveiling expression patterns, mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities of transmembrane protein 106C: From pan-cancers to hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 92437
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/92437.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.92437