Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2025; 17(2): 100724
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100724
Published online Feb 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100724
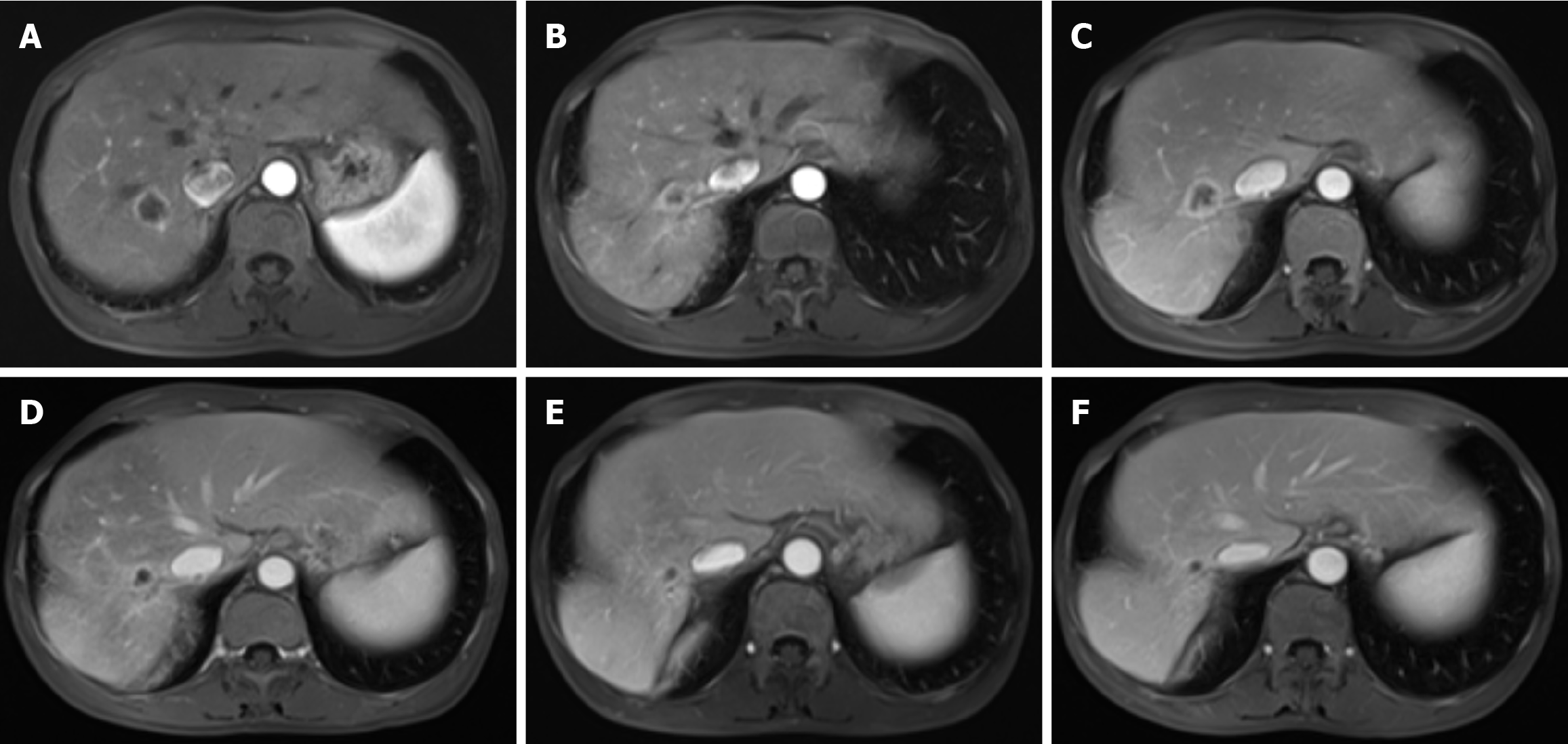
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging of liver metastasis during different anticancer treatment regimens.
A: On November 23, 2022, an enhanced abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a nodular lesion in the right posterior lobe of the liver, with a maximum cross-section of 2.0 cm × 1.9 cm. The lesion exhibited annular enhancement, indicative of a metastatic lesion; B: On February 21, 2023, follow-up MRI revealed a decrease in the size of the nodular lesion to 1.2 cm × 0.9 cm, with persistent annular enhancement; C: On April 11, 2023, MRI revealed an increase in the size of the lesion to 2.0 cm × 1.9 cm, maintaining annular enhancement; D: On July 5, 2023, the lesion was observed to have decreased in size again, measuring 1.4 cm × 1.0 cm, with annular enhancement still present; E: On October 18, 2023, the MRI showed a further reduction in lesion size to 0.9 cm × 0.6 cm, and no enhancement was noted; F: On January 12, 2024, the final MRI revealed no change in lesion size, remaining at 0.9 cm × 0.6 cm, and no enhancement was observed.
- Citation: Luo YH, He T, Lin L, Wang RQ, Cai HX, Hu W. Advanced pancreatic cancer treated with camrelizumab combined with apatinib: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(2): 100724
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i2/100724.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.100724