Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2025; 17(1): 97831
Published online Jan 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i1.97831
Published online Jan 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i1.97831
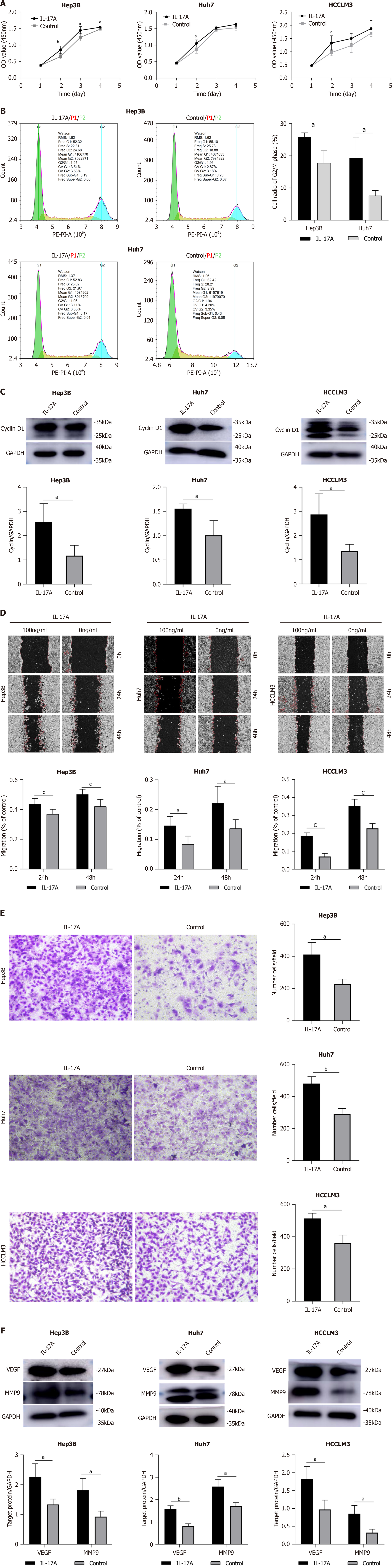
Figure 4 Interleukin-17A promoted hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis.
A: Growth curve showed that interleukin-17A (IL-17A) stimulated cell proliferation, a significant difference that was detected at 24 h after treatment; B: Flow cytometry revealed that, compared with the control, IL-17A significantly increased the proportion of cells in G2/M phase; C: IL-17A elevated cyclinD1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells; D and E: Scratch tests and Transwell assays revealed that IL-17A promoted the migration of HCC cells (× 100 magnification); F: IL-17A increased the protein expression of VEGF and MMP9 in HCC cells. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. PE: Phycoerythrin; PI: Propidium iodide.
- Citation: Yang ZX, Zhang LT, Liu XJ, Peng XB, Mao XR. Interleukin-17A facilitates tumor progression via upregulating programmed death ligand-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(1): 97831
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i1/97831.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i1.97831