Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2025; 17(1): 97831
Published online Jan 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i1.97831
Published online Jan 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i1.97831
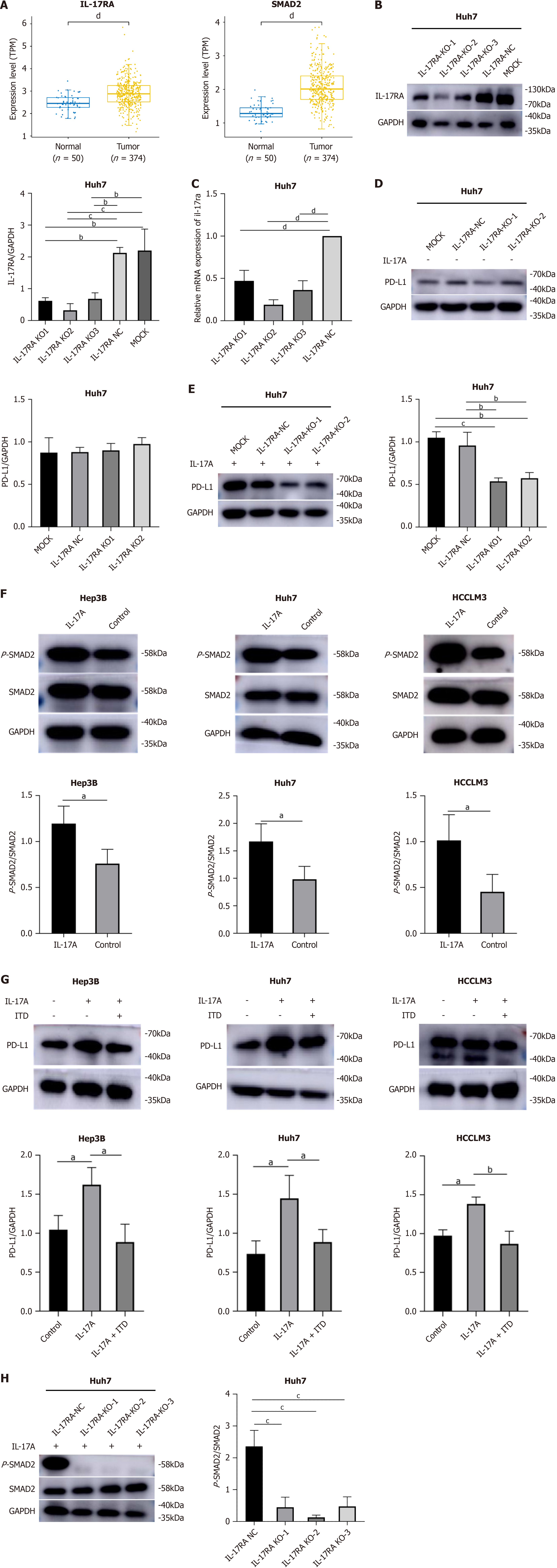
Figure 3 Interleukin-17A upregulated programmed cell death ligand-1 expression via the interleukin-17A receptor/p-small mothers against decapentaplegic 2 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: The Cancer Genome Atlas results revealed that interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and small mothers against decapentaplegic 2 (SMAD2) expression was increased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples compared with normal tissue samples; B: Interleukin-17A receptor (IL-17RA) protein expression level after knockout (KO) of IL-17RA in Huh7 cells; C: IL-17RA mRNA levels after KO of IL-17RA in Huh7 cells; D: IL-17RA KO alone did not affect programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression in Huh7 cells; E: IL-17A-induced PD-L1 expression was reversed by IL-17RA KO in Huh7 cells; F: IL-17A increased the level of phosphorylated (p)-SMAD2 in HCC cells; G: IL-17A-induced PD-L1 expression was inhibited by pretreatment with transforming growth factor-beta signal pathway inhibitor in HCC cells; H: IL-17RA KO sharply reversed IL-17A-induced p-SMAD2 expression in Huh7 cells. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; dP < 0.0001. ITD: TGF-beta signal pathway inhibitor; MOCK: Blank control; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Yang ZX, Zhang LT, Liu XJ, Peng XB, Mao XR. Interleukin-17A facilitates tumor progression via upregulating programmed death ligand-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(1): 97831
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i1/97831.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i1.97831