Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2024; 16(9): 3913-3931
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3913
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3913
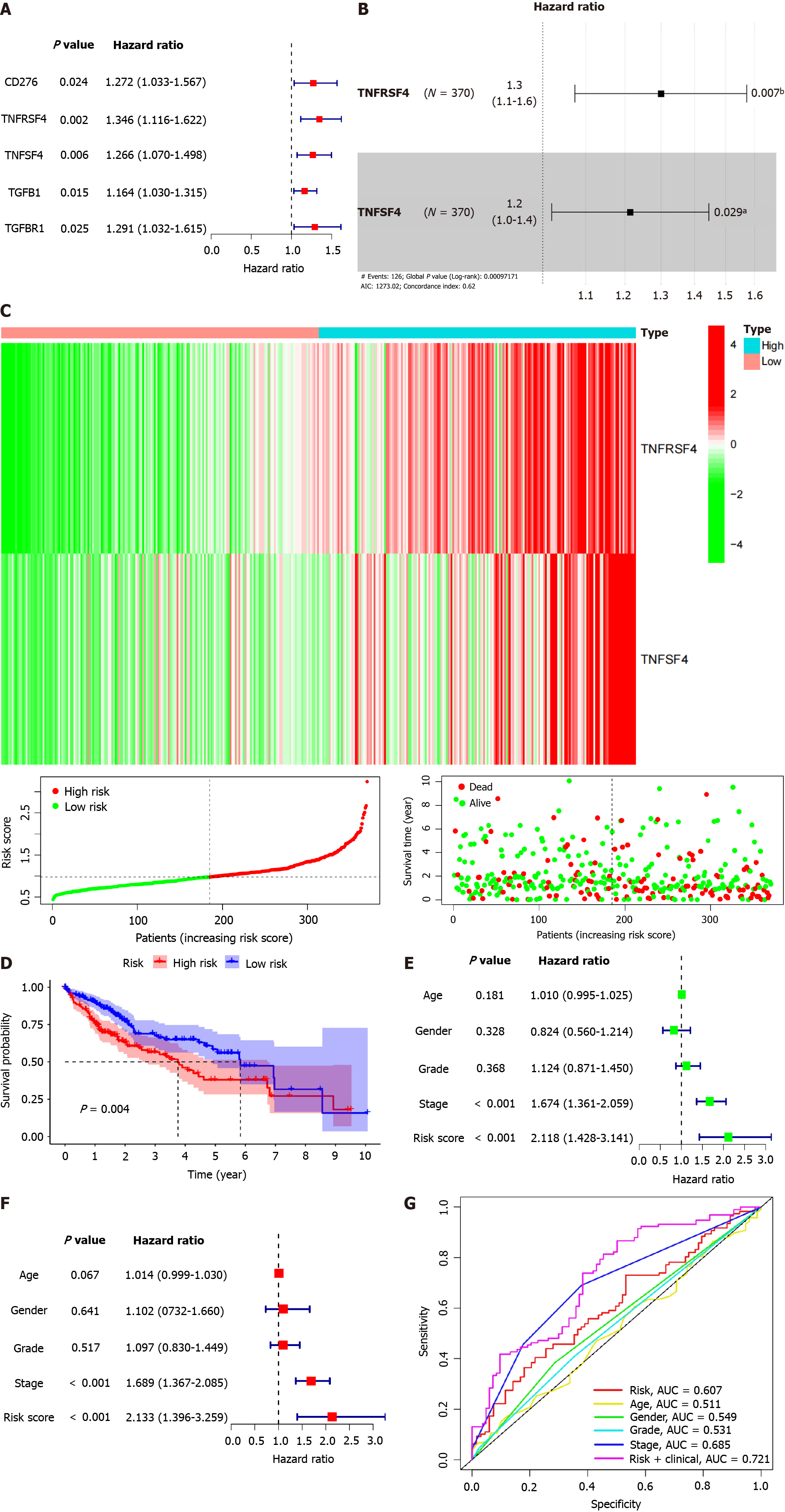
Figure 4 Risk model construction based on protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor 2-associated immunomodulators in hepato
- Citation: Li HY, Jing YM, Shen X, Tang MY, Shen HH, Li XW, Wang ZS, Su F. Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor II: A possible biomarker of poor prognosis and mediator of immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(9): 3913-3931
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i9/3913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3913