Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2024; 16(9): 3887-3897
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3887
Published online Sep 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3887
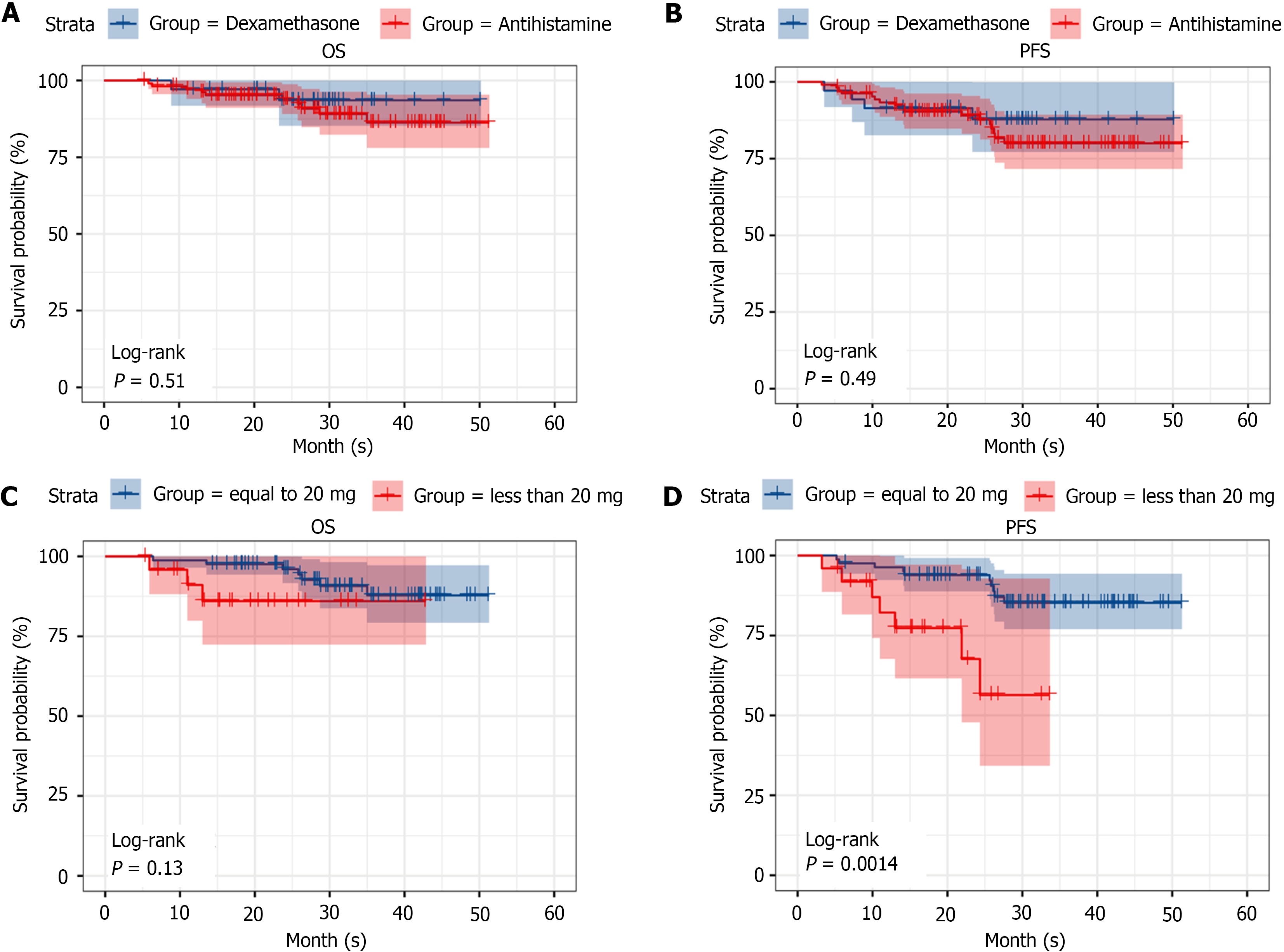
Figure 5 Long-term efficacy assessment.
A: Comparison of overall survival (OS) between the dexamethasone and antihistamine groups. The log-rank test P value is 0.51, indicating no statistically significant difference in OS between the two groups; B: Comparison of progression-free survival (PFS) between the dexamethasone and antihistamine groups. The log-rank test P value is 0.49, indicating no statistically significant difference in PFS between the two groups; C: Comparison of OS between the < 20 mg dexamethasone group and the 20 mg dexamethasone group. The log-rank test P value is 0.13, indicating no statistically significant difference in OS between the two groups; D: Comparison of PFS between the < 20 mg dexamethasone group and the 20 mg dexamethasone group. The log-rank test P value is 0.0014, indicating a statistically significant difference in PFS between the two dosage groups, suggesting that 20 mg of dexamethasone may lead to better PFS outcomes. OS: Overall survival; PFS: Progression-free survival.
- Citation: Huang YH, Yang GZ, Chen HG, Li XJ, Wu YH, Zhang K, Xu JN, Zhang J. Impact of baseline steroids on the efficacy of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(9): 3887-3897
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i9/3887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3887