Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2024; 16(8): 3651-3671
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3651
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3651
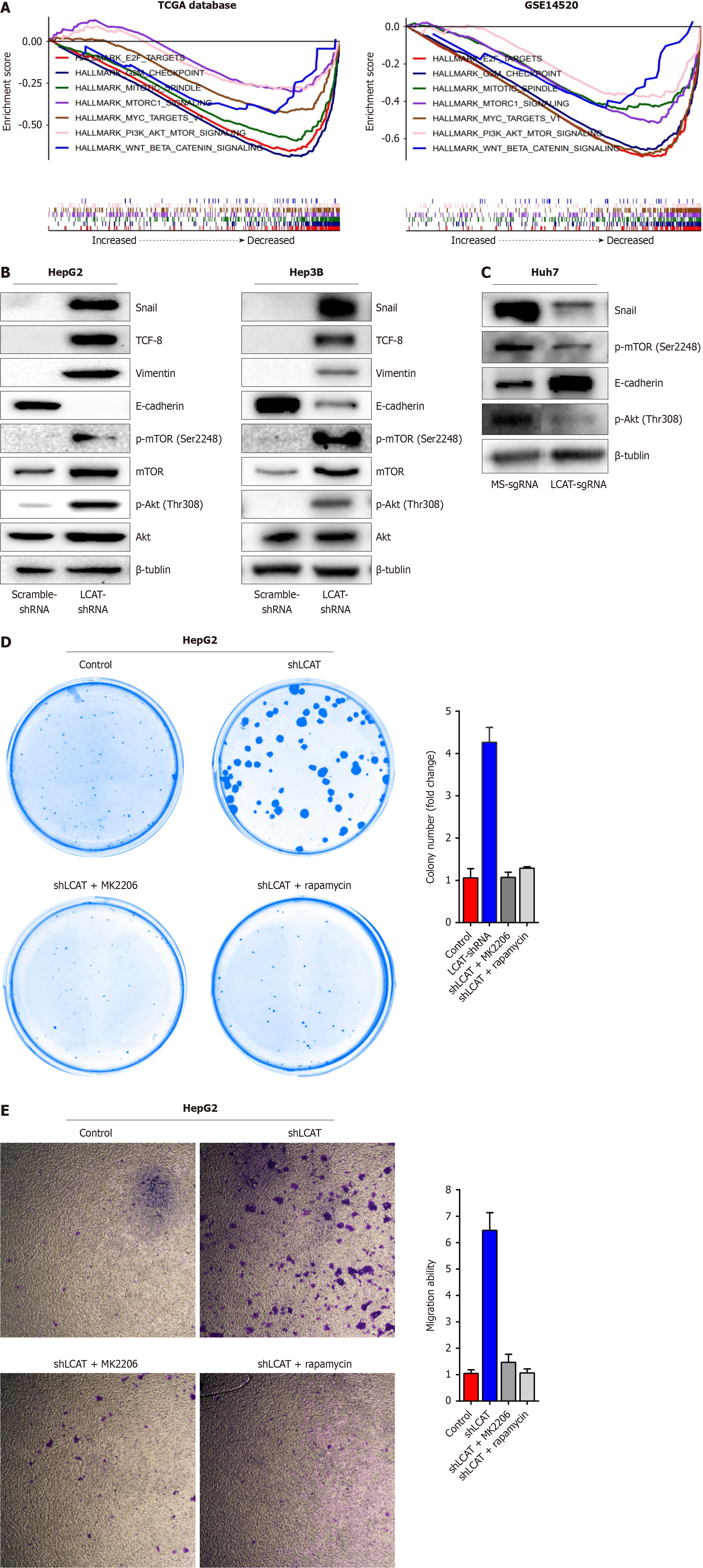
Figure 4 Downregulation of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchy
- Citation: Li Y, Jiang LN, Zhao BK, Li ML, Jiang YY, Liu YS, Liu SH, Zhu L, Ye X, Zhao JM. Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase is a potential tumor suppressor and predictive marker for hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(8): 3651-3671
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i8/3651.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3651