Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2024; 16(8): 3651-3671
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3651
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3651
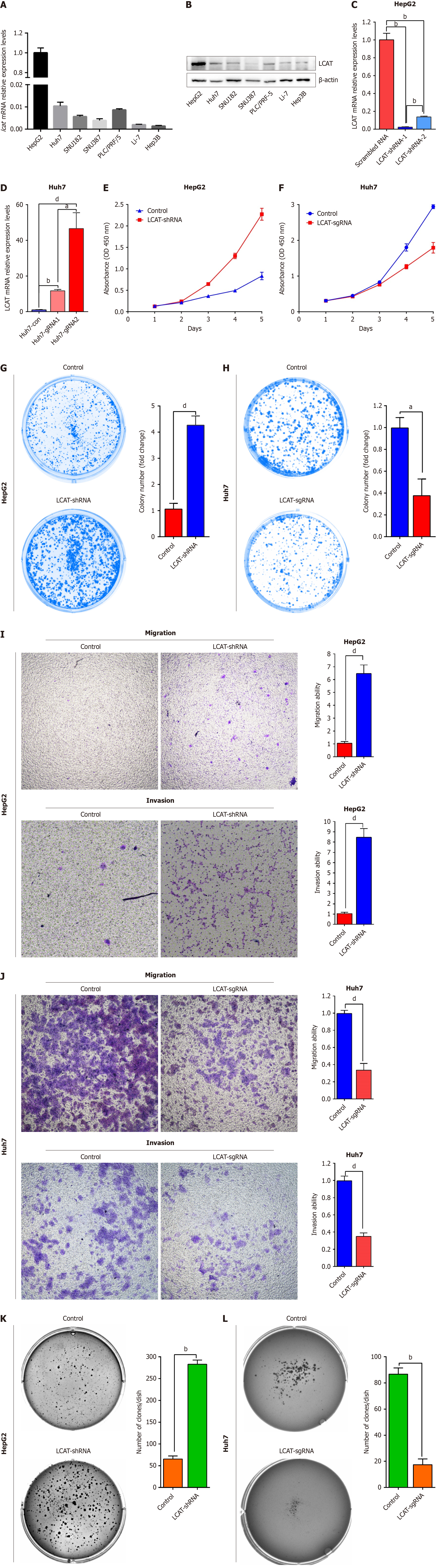
Figure 2 Roles of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase in inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma cells growth and metastasis in vitro.
A and B: Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) expression examined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting in seven hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines; C and D: Confirmation of LCAT knockdown or overexpression in HCC cells by qRT-PCR; E and F: Growth curves of HepG2 and LCAT knocked down HepG2 (E) or Huh7 and LCAT overexpressed Huh7 cells (F); G and H: Colony formation assays of HepG2 and LCAT knocked down HepG2 (G) or Huh7 and LCAT overexpressed Huh7 cells (H). The bar graphs illustrate the quantification of the colony formation assay. Student’s t test was used; I and J: Cell migration and invasion assays of HepG2 and LCAT knocked down HepG2 (I) or Huh7 and LCAT overexpressed Huh7 cells (J). The graphs depict the number of migration and invasive cells. Student’s t test was used; K and L: Soft agar assays for HepG2 and LCAT knocked down HepG2 (K) or Huh7 and LCAT overexpressed Huh7 cells (L). Representative images are shown (left). The numbers of colonies are present in the right panel. aP < 0.01, bP < 0.0001, dP < 0.001. LCAT: Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase.
- Citation: Li Y, Jiang LN, Zhao BK, Li ML, Jiang YY, Liu YS, Liu SH, Zhu L, Ye X, Zhao JM. Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase is a potential tumor suppressor and predictive marker for hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(8): 3651-3671
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i8/3651.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3651