Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2024; 16(8): 3600-3623
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3600
Published online Aug 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3600
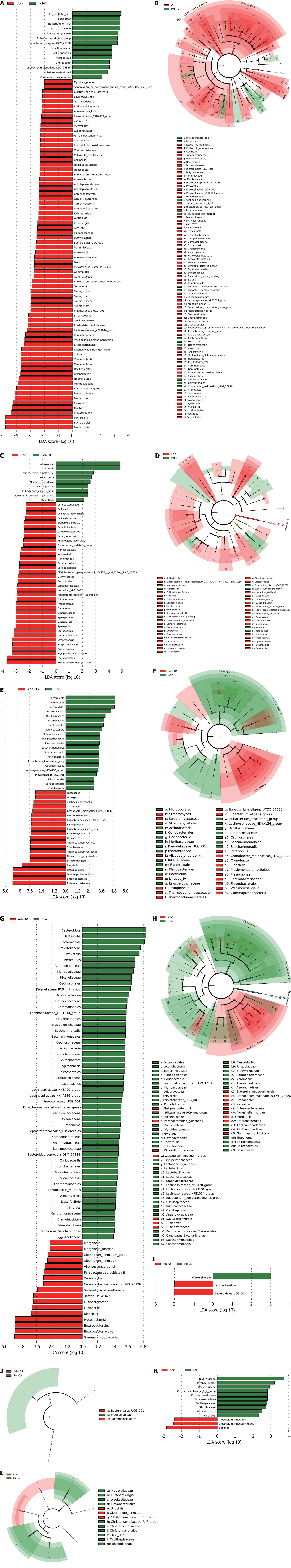
Figure 7 Diagram of different bacteria communities.
A-L: These plots were derived from the linear discriminant analysis (LDA), which was employed to rank identified species. LDA plots showcase groups of biomarkers, with the bar graph lengths indicating the effect magnitude of these differential species. Only results with LDA scores ≥ 2 and a significance level of aP < 0.05 were retained for these visualizations (A, C, E, G, I, and K); the linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) analysis began with a Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test applied to all group samples, aiming to identify differentially abundant species (aP < 0.05). Subsequently, these species were compared pairwise between groups using the Wilcoxon rank sum test (B, D, F, H, J, and L). The outcome is an evolutionary branching diagram, which plots these divergent species on a taxonomically structured tree. In this diagram, circles radiate from the inner to the outer layers, representing taxonomic levels from phylum to species. The default display extends to the species level. The circle diameters correspond to the relative abundance of taxa, and different color nodes highlight groups significantly enriched in bacterial bacteria, thus underlining the distinctiveness between groups. Species with non-significant differences are not displayed by default. A and B, C and D, E and F, and G and H represent LDA score and LEfSe analysis of non-adenomatous polyps (Pol)-0.5, Pol-10, adenomatous polyps (Ade)-0.5, and Ade-10 vs Con, respectively; I and J represent LDA score and LEfSe analysis of Pol-0.5 vs Ade-0.5; K and L represent LDA score and LEfSe analysis of Pol-10 vs Ade-10. Ade: Adenomatous polyps; Pol: Non-adenomatous polyps; Con: Control; LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
- Citation: Yin LL, Qi PQ, Hu YF, Fu XJ, He RS, Wang MM, Deng YJ, Xiong SY, Yu QW, Hu JP, Zhou L, Zhou ZB, Xiong Y, Deng H. Dysbiosis promotes recurrence of adenomatous polyps in the distal colorectum. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(8): 3600-3623
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i8/3600.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3600