Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2024; 16(7): 3350-3356
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3350
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3350
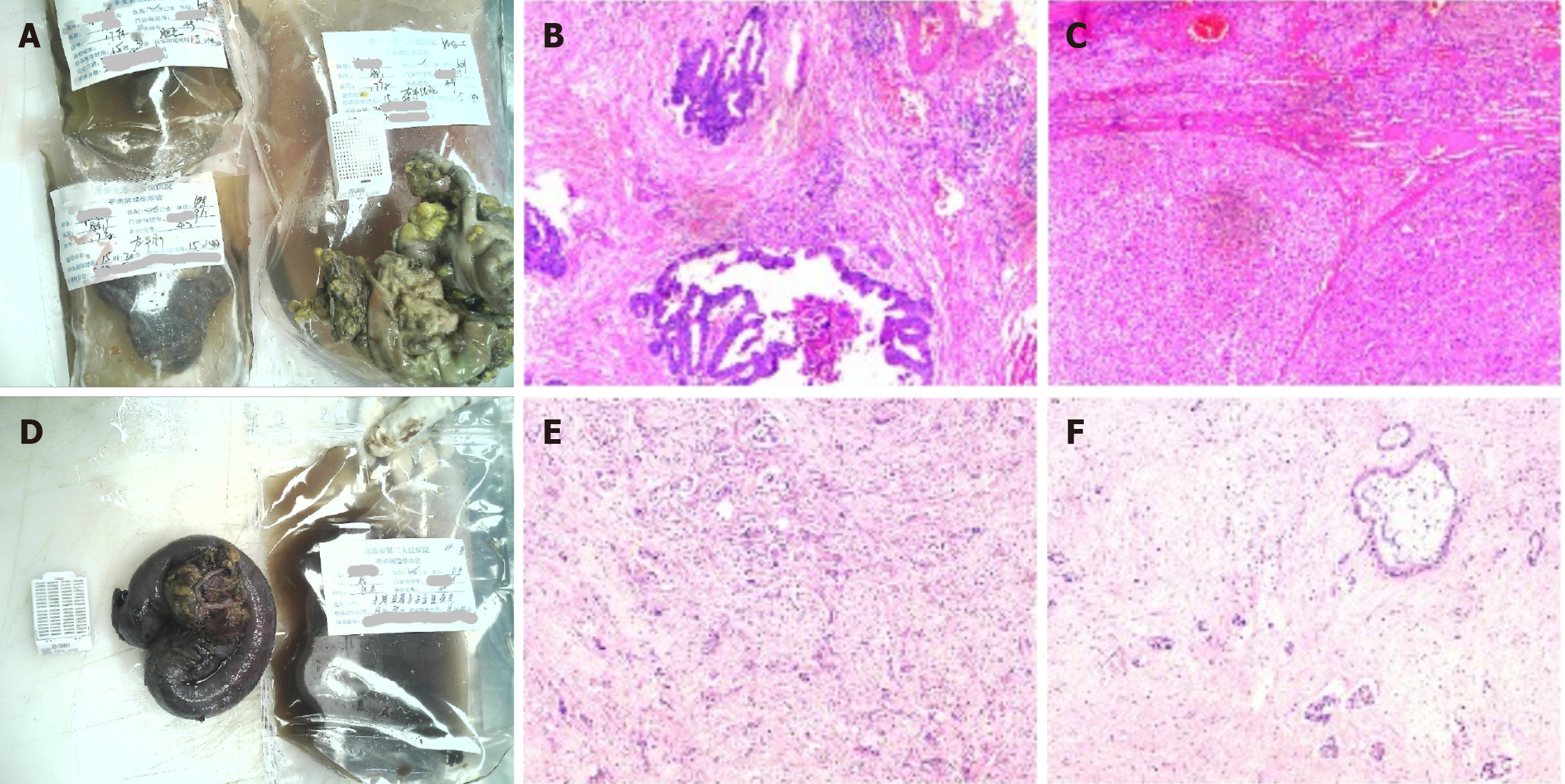
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the pathological results of the lesions after the first and second operations.
A: Gross images of the first surgery specimen; B and C: Light microscopic images of the first surgery specimen with the following immunohistochemical results: CD34+, D2-40+, CK7-, CK19-, hepatocyte+, CD34+, endothelial vascularization of hepatic sinusoids, carcinoembryonic antigen-. Pathological diagnosis: (Right hemicolon) low-moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma infiltrating the plasma membrane layer in the fibro-fatty tissues (there was choroidal carcinoma embolus and there were no nerve invasion, negative margins, or metastasis in the lymph nodes); (left liver) moderately differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (there was no choroidal carcinoma embolus or nerve invasion, negative margins, or cirrhotic changes); D: Gross images of the second surgical specimen; E and F: Light microscopic images of the second surgical procedure. The immunohistochemical results were as follows: Tumor cells CK7+, CK20-, villin+, hepatocyte few cells+, glypican-3-, CK8/18+, CDX2 few+, D2-40 lymphatic vessels+, CD34 vascular+, Ki67 hotspot area+ in about 50%-60%. Pathological diagnosis: (Terminal ileum and occupying lesion) moderately-lowly differentiated adenocarcinoma (the tumor invaded the intestinal wall tissue from the plasma membrane upward and focally invaded the mucosal musculature. Combined with the history and immunohistochemistry results, the colonic origin and hepatocellular carcinoma origin were not supported at this time, and pancreatic origin was considered. Moreover, vascular cancer embolism and nerve invasion could be observed in the interior).
- Citation: Wan DD, Li XJ, Wang XR, Liu TX. Metachronous multifocal carcinoma: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(7): 3350-3356
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i7/3350.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3350