Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2024; 16(7): 3270-3283
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3270
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3270
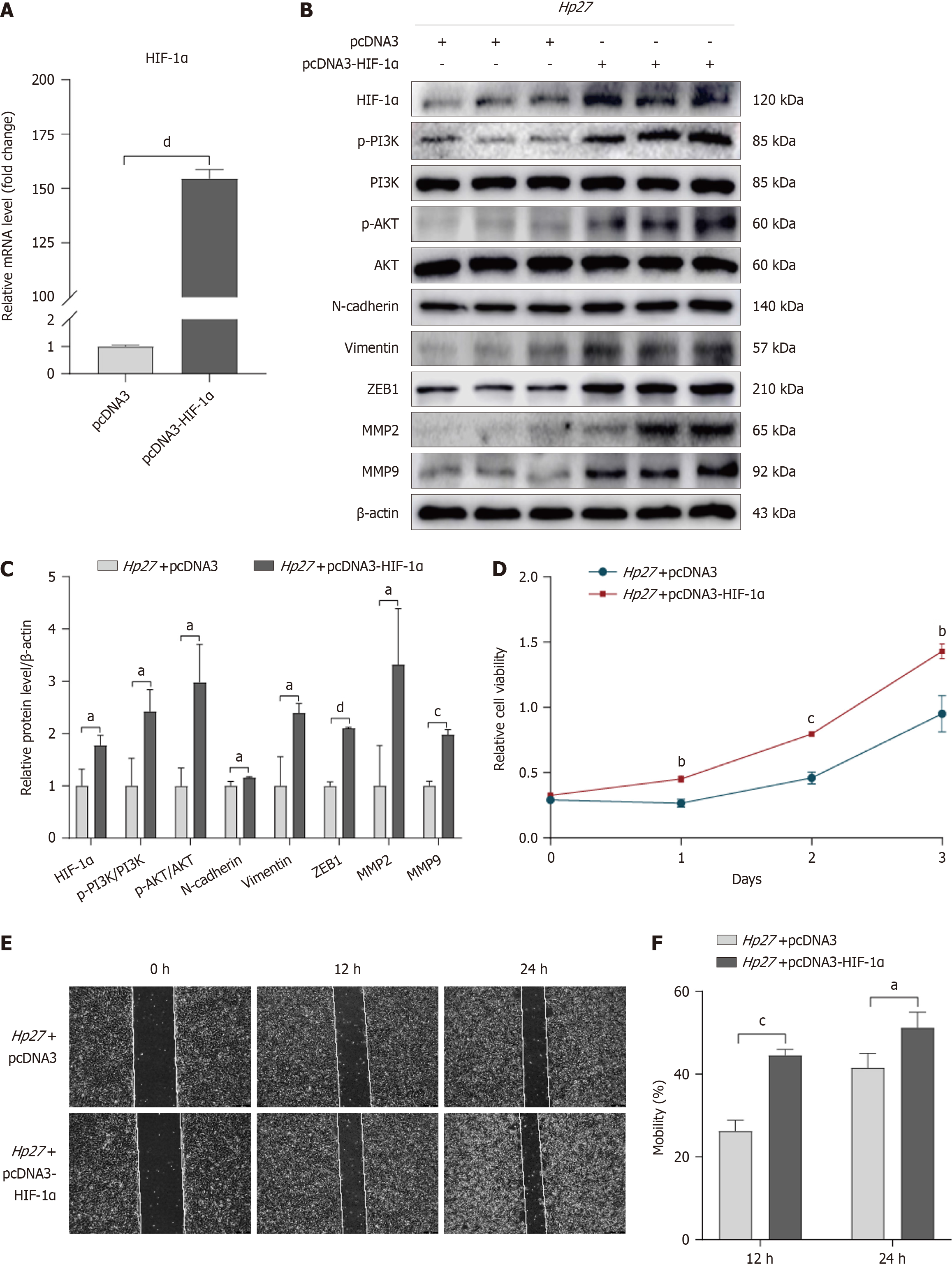
Figure 2 Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α overexpression promotes the activation of PI3K/AKT pathway and the malignant behaviors of cells.
A: Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction showed that hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) plasmid was successfully transfected into gastric epithelial cells; B and C: Protein levels were analyzed by Western blot, including HIF-1α, p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT, AKT, N-cadherin, Vimentin, ZEB1, MMP2, and MMP9, all normalized to β-actin. These proteins respectively represented the PI3K/AKT pathway, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and cell invasion ability; D: Cell counting kit-8 assay was utilized to evaluate cell viability; E and F: Wound healing assay was conducted to test the migration ability. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001, compared with pcDNA3 or Hp27 + pcDNA3 group. Hp27: H. pylori 27 strain; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α.
- Citation: An TY, Hu QM, Ni P, Hua YQ, Wang D, Duan GC, Chen SY, Jia B. N6-methyladenosine modification of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulates Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer via the PI3K/AKT pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(7): 3270-3283
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i7/3270.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3270