Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2024; 16(7): 3211-3229
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3211
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3211
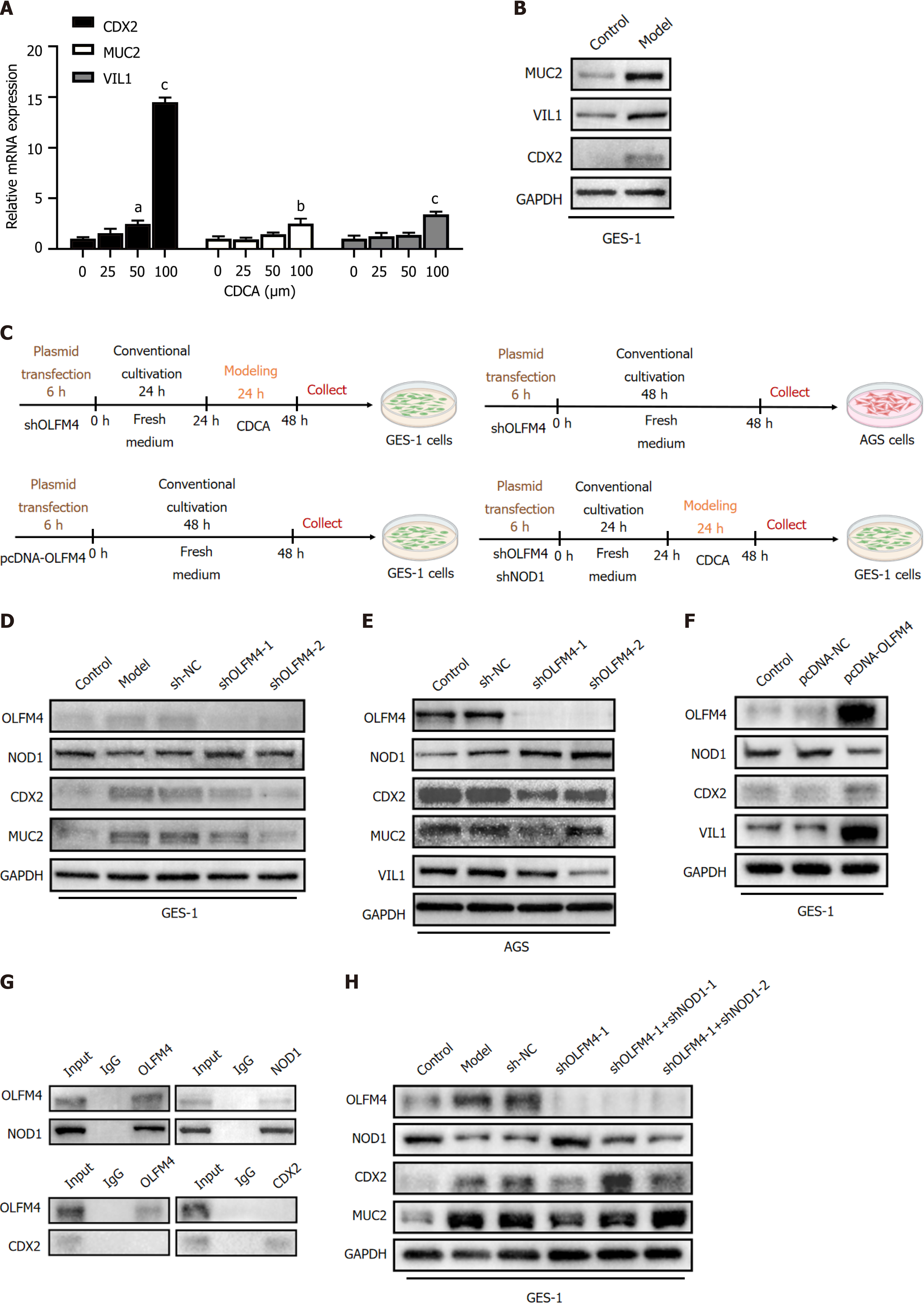
Figure 2 Olfactomedin 4 exhibited direct binding and subsequent down-regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1, thereby sustaining the activation of caudal-type homeobox gene 2 and promoting the progression of intestinal metaplasia.
A: Relative mRNA expressions of caudal-type homeobox gene 2 (CDX2), MUCIN 2 (MUC2), and villin 1 (VIL1) on stimulation of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) in GES-1 cells (n = 3); B: Western blot (WB) detection of MUC2, VIL1, and CDX2 in GES-1 cells treated with CDCA (100 μM) for 24 h; C: Timeline of the cell experiments design for pathway regulatory verification; D: Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) targeting olfactomedin 4 (OLFM4) were transfected to GES-1 cells. Subsequently, the cells were treated with CDCA (100 μM) for 24 h. WB detection of OLFM4, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1), CDX2, and MUC2; E: AGS cells were transfected with OLFM4 shRNAs. WB detection of OLFM4, NOD1, CDX2, MUC2, and VIL1; F: OLFM4-pcDNAs were transfected to GES-1 cells. WB detection of OLFM4, NOD1, CDX2, and VIL1; G: Co-immunoprecipitation detection of the interaction between OLFM4 and NOD1, and the interaction between OLFM4 and CDX2 in GES-1 cells; H: OLFM4 and NOD1 shRNAs were co-transfected to GES-1 cells. Subsequently, the cells were treated with CDCA (100 μM) for 24 h. WB detection of OLFM4, NOD1, CDX2, and MUC2. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs control group. OLFM4: Olfactomedin 4; NOD1: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1; CDX2: Caudal-type homeobox gene 2; MUC2: MUCIN 2; VIL1: Villin 1; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid.
- Citation: Zhou DS, Zhang WJ, Song SY, Hong XX, Yang WQ, Li JJ, Xu JQ, Kang JY, Cai TT, Xu YF, Guo SJ, Pan HF, Li HW. Weiwei Decoction alleviates gastric intestinal metaplasia through the olfactomedin 4/nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1/caudal-type homeobox gene 2 signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(7): 3211-3229
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i7/3211.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3211