Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2024; 16(7): 3118-3157
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3118
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3118
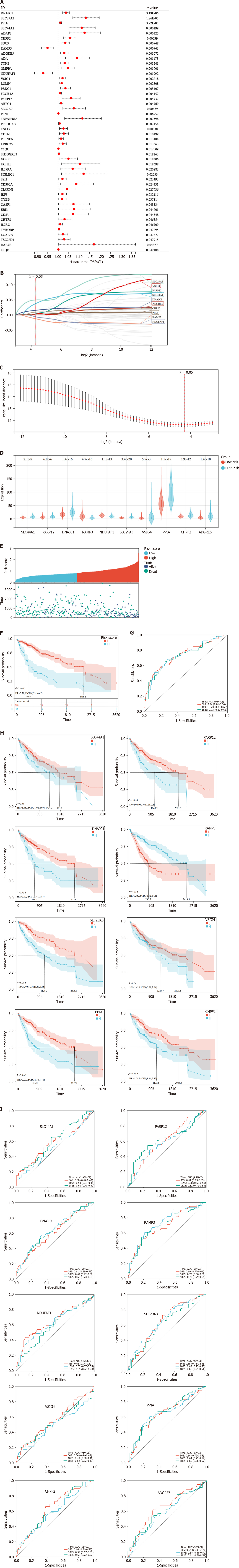
Figure 2 Identification of prognostic immune-related genes for hepatocellular carcinoma ablation therapy using machine learning.
A: The forest plot shows 48 significant independent risk genes (IRGs) based on single-factor Cox regression analysis; B: Seven candidate genes were identified through least absolute shrinkage and selection operator analysis (LASSO) analysis with a lambda value of 0.04; C: Partial likelihood deviance of the LASSO coefficient distribution with a lambda value of 0.04; D: Violin plots showing the expression of 10 IRGs in patients at different risk levels; E: The risk levels and survival status of 365 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients are displayed; F: Kaplan-Meier curves were created to compare the differences in prognosis between the high-risk and low-risk groups based on the risk scores derived from LASSO analysis; G: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis at 1, 3, and 5-year time points based on the risk scores derived from LASSO analysis; H: Survival curve analysis for the 10 IRGs; I: ROC analysis of the 10 IRGs at 1, 3, and 5 years. SLC44A1: Solute carrier family 44 member 1; PARP12: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 12; DNAJC1: DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C1; RAMP3: Receptor activity modifying protein 3; NDUFAF1: NADH: Ubiquinone oxidoreductase complex assembly Factor 1; SLC29A3: Solute carrier family 29 member 3; VSIG4: V-Set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4; PPIA: Peptidylprolyl isomerase A; CHPF2: Chondroitin polymerizing factor 2; ADGRE5: Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor E5.
- Citation: Cao Y, Li PP, Qiao BL, Li QW. Kombo knife combined with sorafenib in liver cancer treatment: Efficacy and safety under immune function influence. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(7): 3118-3157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i7/3118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3118