Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2024; 16(7): 3055-3068
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3055
Published online Jul 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3055
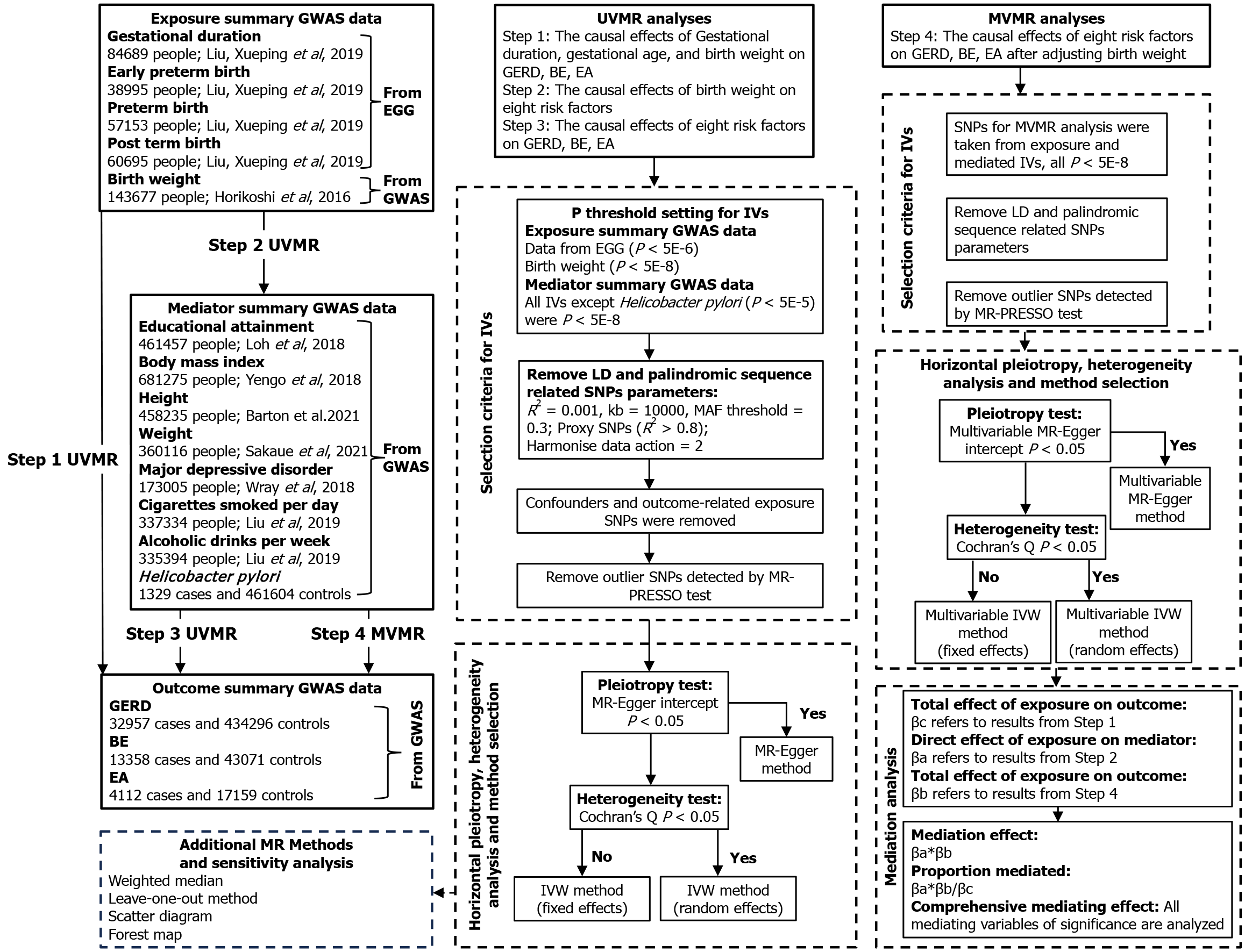
Figure 1 Flowchart of Mendelian randomization analyses in this study.
Step 1: The causal effects of gestational duration, gestational age, and birth weight on gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Barrett’s esophagus (BE), esophageal adenocarcinoma (EA); Step 2: The causal effects of birth weight on eight risk factors; Step 3: The causal effects of eight risk factors on GERD, BE, EA; Step 4: The causal effects of eight risk factors on GERD, BE, EA after adjusting birth weight. BE: Barrett’s esophagus; EA: Esophageal adenocarcinoma; EGG: Early Growth Genetics; GWAS: Genome-wide association study; IVs: Instrumental variables; IVW: Inverse variance weighted; MR-PRESSO: MR-Pleiotropy RESidual sum and outlier; UVMR: Univariable Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; MVMR: Multivariable Mendelian randomization; LD: Linkage disequilibrium.
- Citation: Ruan LC, Zhang Y, Su L, Zhu LX, Wang SL, Guo Q, Wan BG, Qiu SY, Hu S, Wei YP, Zheng QL. Causal effects of genetic birth weight and gestational age on adult esophageal diseases: Mendelian randomization study. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(7): 3055-3068
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i7/3055.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3055