Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2769-2780
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769
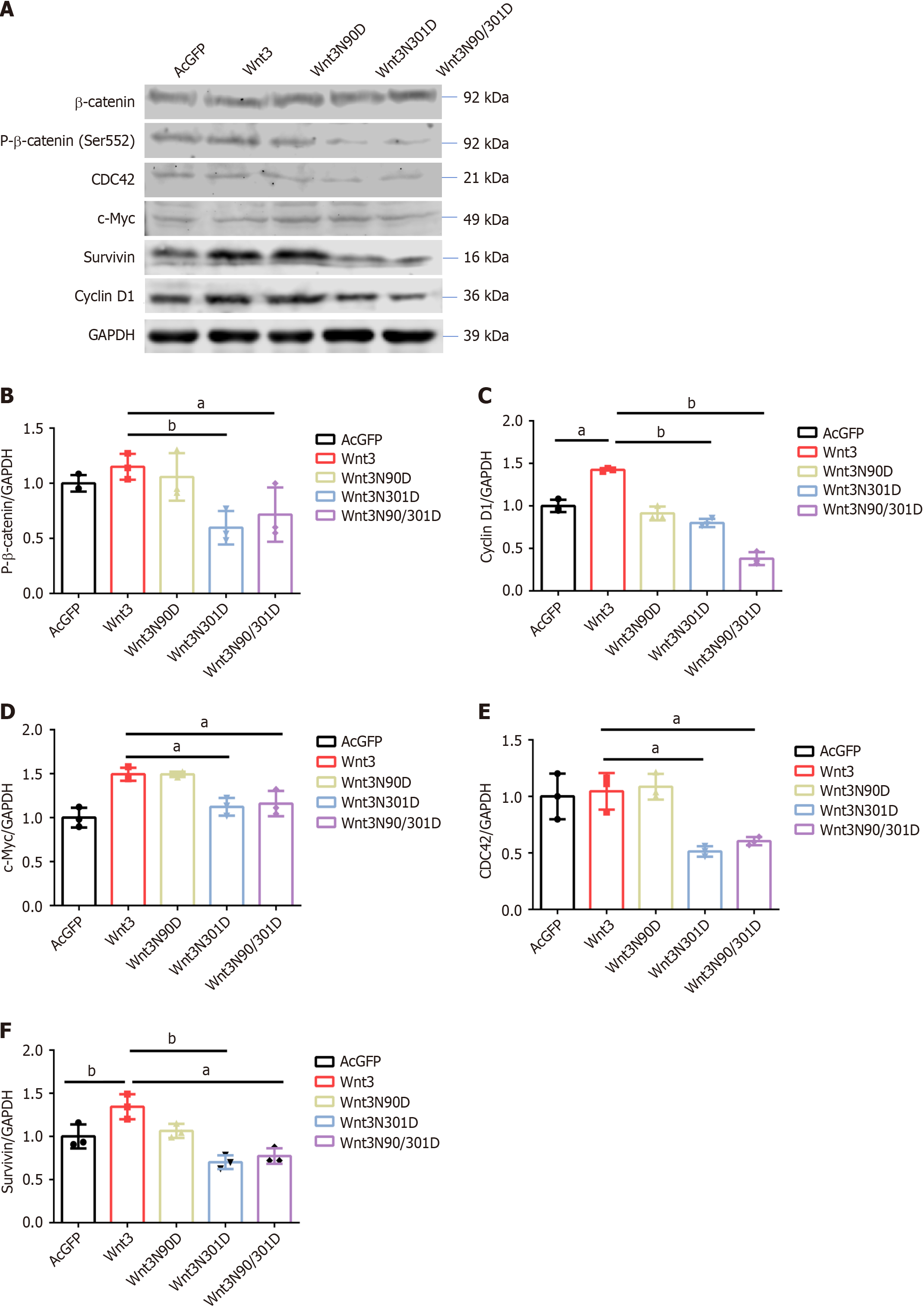
Figure 3 Site-directed mutations in Wnt3 affect signaling pathways downstream.
A: The effect of different Wnt3 N-glycosylation-deficient mutants on the expression of effector molecules in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was assessed by Western blot analysis; B: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the p-β-catenin/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; C: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the Cyclin D1/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; D: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the C-myc/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; E: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the CDC42/GAPDH values were compared between the groups; F: ImageJ software was used to detect the IntDen values, and the Survivin/GAPDH values were compared between the groups. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. GFP: Green fluorescent protein.
- Citation: Zhang XZ, Mo XC, Wang ZT, Sun R, Sun DQ. N-glycosylation of Wnt3 regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2769-2780
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2769.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769