Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2769-2780
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769
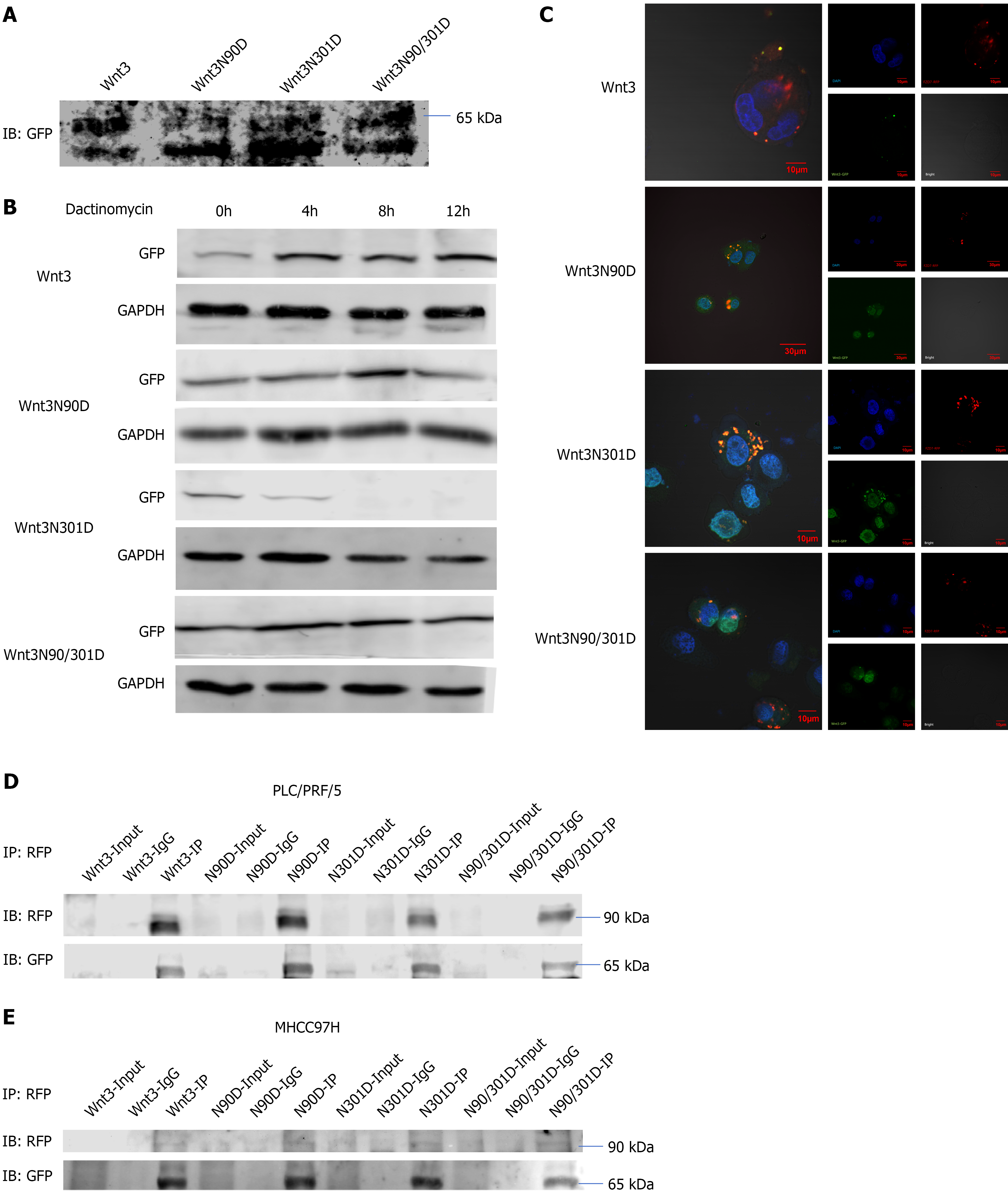
Figure 2 N-glycosylation affects the stability of Wnt3 and its ability to bind to the FZD7 receptor.
A: The medium was replaced with serum-free medium 36 h after the transfection of PLC/PRF/5 cells. Twenty-four hours later, the medium was collected, ultrafiltration tubes were used for concentration, and then the samples were prepared for detection; B: At 36 h after the transfection of PLC/PRF/5 cells, actinomycin D was added, and the working concentration was 20 μg/mL; C: Localization of Wnt3 and its N-glycosylation deletion mutants (green) and FZD7 (red) in PLC/PRF/5 cells. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); D and E: In PLC/PRF/5 and MHCC97H cells, anti-RFP was used for pull-down, and anti-GFP was used for detection. GFP: Green fluorescent protein; RFP: Red fluorescent protein; IP: Immunoprecipitation; IB: Immunoblotting.
- Citation: Zhang XZ, Mo XC, Wang ZT, Sun R, Sun DQ. N-glycosylation of Wnt3 regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2769-2780
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2769.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769