Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2742-2756
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742
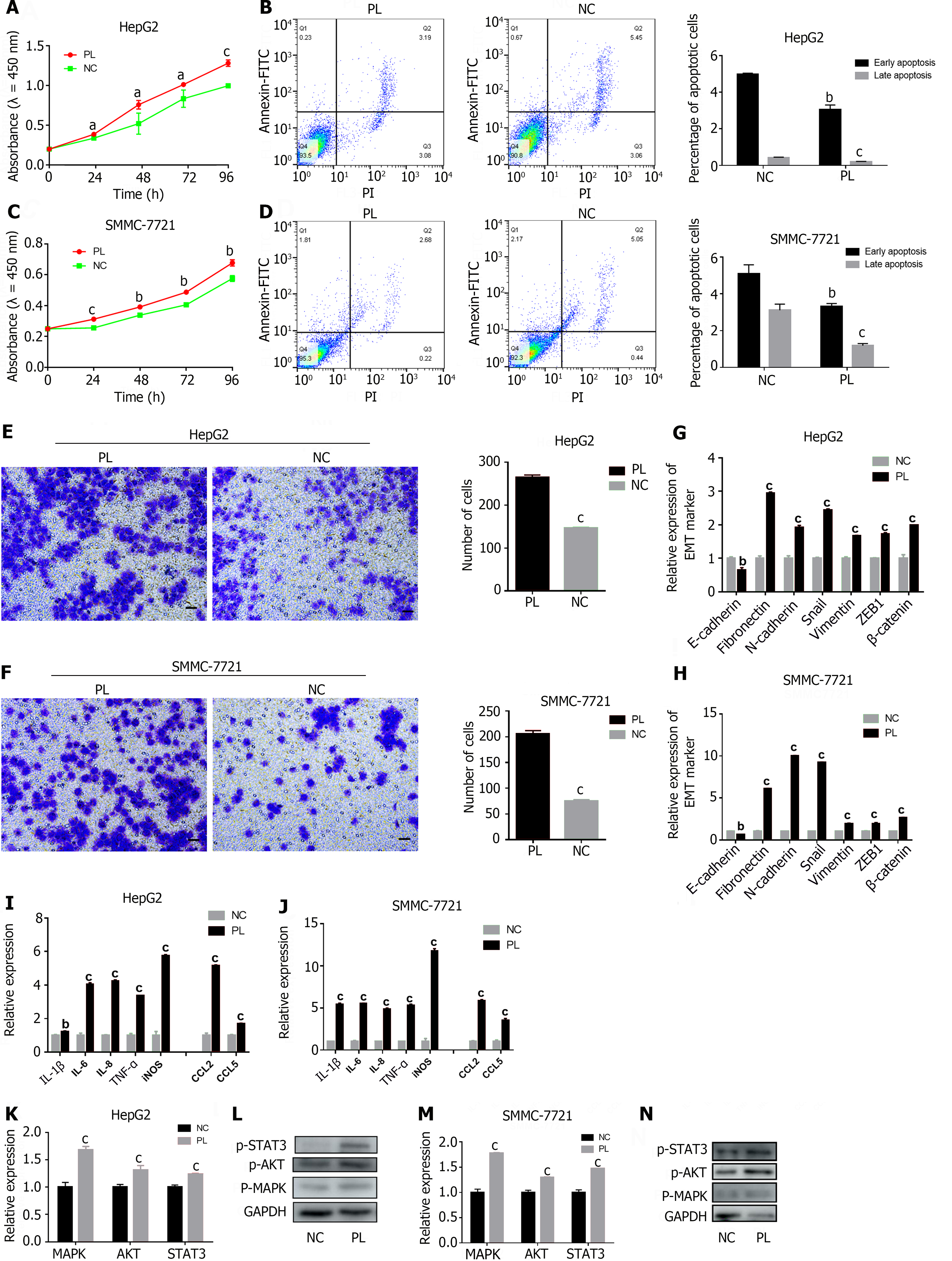
Figure 4 Activated platelets activate the MAPK/AKT/STAT3 signaling axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A and C: CCK-8 analysis was used to detect the effect of platelet lysis buffer (PL) on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells; B and D: The effect of PL on apoptosis detected by flow cytometry is shown on the left, and the corresponding statistical results are shown on the right; E and F: Transwell assays were used to detect the effect of PL on the invasion ability of HCC cells, and the statistical results are shown on the right. 200 × magnification, scale bar: 200 μm; G and H: Real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to detect the effect of PL on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition ability of HCC cells; I and J: RT-PCR was used to detect the effect of PL on cytokine secretion by HCC cells; K and M: RT-PCR was used to detect the effect of PL on the expression of genes involved in the MAPK/AKT/STAT3 signaling axis; L and N: Western blot was used to detect the effect of PL on the protein expression of p-MAPK, p-AKT and p-STAT3. The figure shows the mean ± SD deviation of the experimental results, with asterisks denoting significant differences between the two groups (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001). NC: Negative control; PL: Platelet lysis buffer; Annexin V-FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled Annexin V; PI: Propidium iodide.
- Citation: Zhao LJ, Wang ZY, Liu WT, Yu LL, Qi HN, Ren J, Zhang CG. Aspirin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting platelet activity. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2742-2756
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2742.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742