Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2742-2756
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742
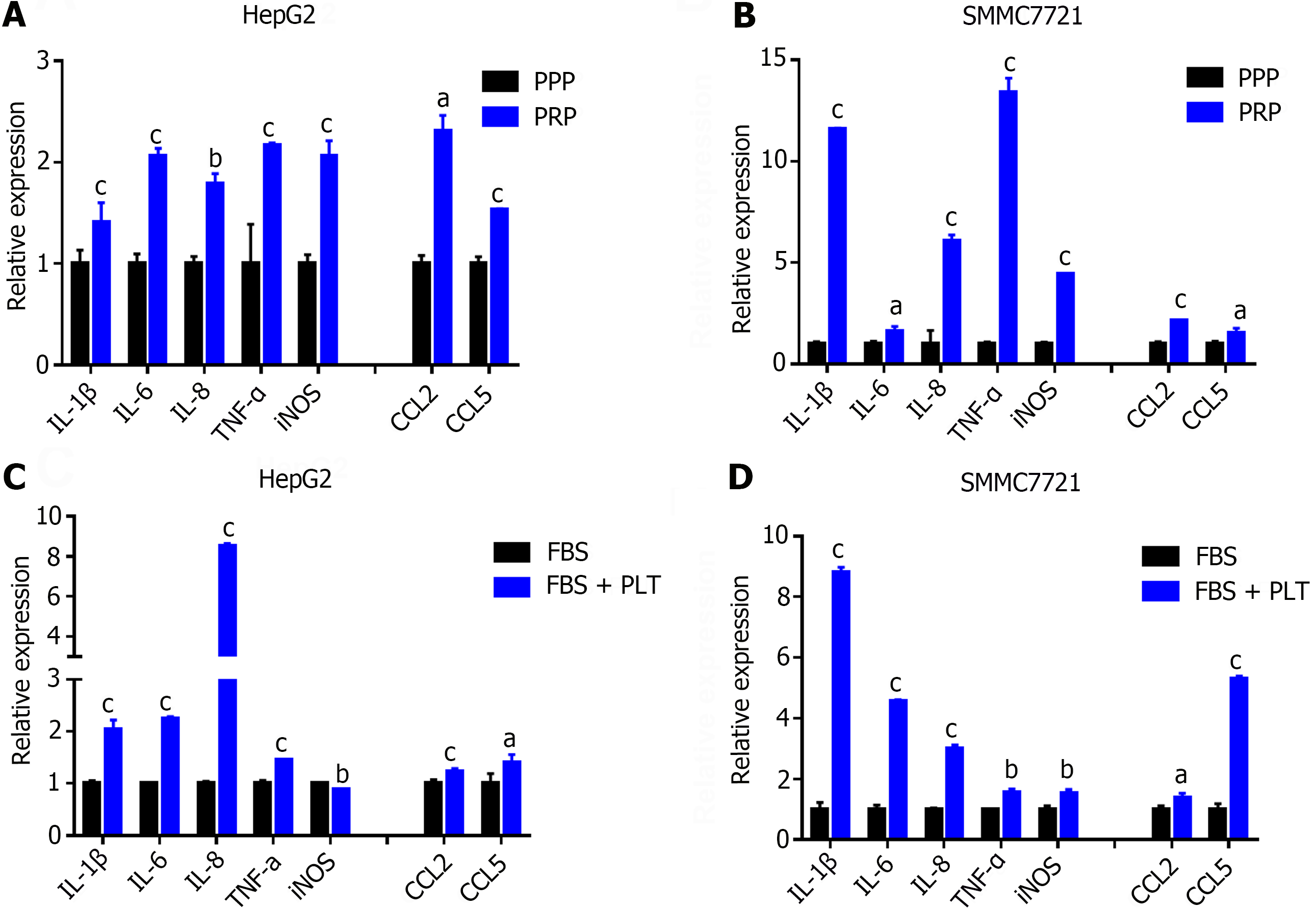
Figure 3 Platelets promote the formation of an inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A and B: Real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to detect the effects of platelet plasma and platelet-rich plasma on the expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and iNOS) and chemokines (CCL2, CCL5) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells; C and D: RT-PCR was used to detect the effect of platelets (PLTs) on the expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and iNOS) and chemokines (CCL2 and CCL5) in HCC cells. The figure shows the mean ± SD of the experimental results, with asterisks denoting significant differences between the two groups (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001). PPP: Platelet plasma; PRP: Platelet-rich plasma; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; PLT: Platelets.
- Citation: Zhao LJ, Wang ZY, Liu WT, Yu LL, Qi HN, Ren J, Zhang CG. Aspirin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting platelet activity. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2742-2756
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2742.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742