Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2742-2756
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742
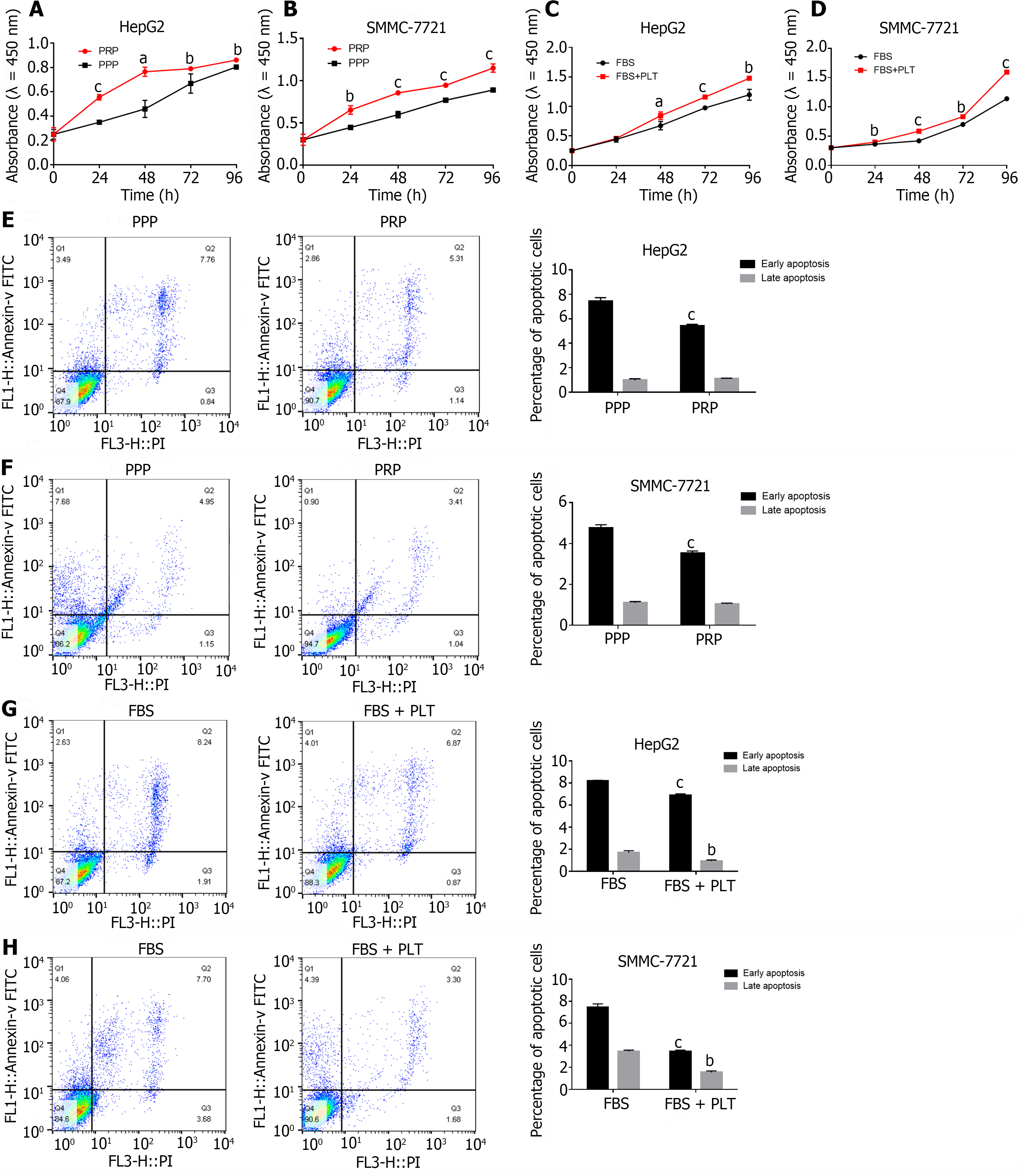
Figure 1 Platelets promote the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A and B: CCK-8 assay was used to analyze the effects of platelet plasma (PPP) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells; C and D: CCK8 analysis of the effect of platelets (PLTs) on HCC cell proliferation; E and F: Flow cytometry was used to detect the effects of PPP and PRP on apoptosis in HCC cells, and the results of the statistical analysis of early apoptosis and late apoptosis are shown on the right; G and H: Flow cytometry was used to detect the effect of PLTs on HCC apoptosis, and the results of the statistical analysis of early apoptosis and late apoptosis are shown on the right. The figure shows the mean ± SD of the experimental results, with asterisks denoting significant differences between the two groups (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001). Annexin V-FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled Annexin V; PI: Propidium iodide; PPP: Platelet plasma; PRP: Platelet-rich plasma; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; PLT: Platelets.
- Citation: Zhao LJ, Wang ZY, Liu WT, Yu LL, Qi HN, Ren J, Zhang CG. Aspirin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting platelet activity. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2742-2756
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2742.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2742