Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2646-2662
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2646
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2646
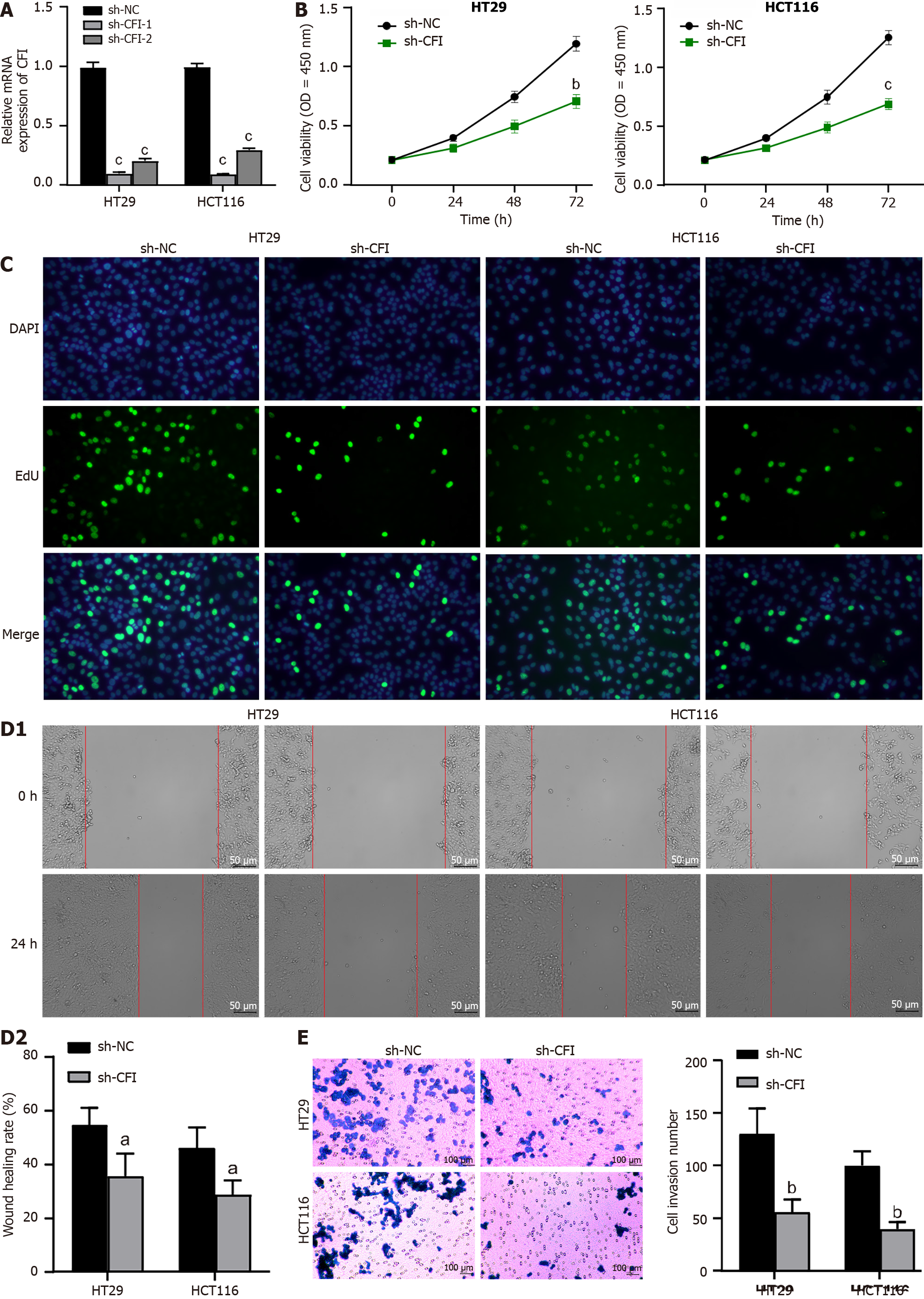
Figure 4 Knockdown of complement factor I inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells.
A: Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of complement factor I (CFI) silencing; B: CCK-8 assay was performed to assess the viability of colon cancer cells in each group; C: Cell proliferation capability was measured by 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine assay; D: At 0 h and 24 h, the area inside the scratched area was measured, and the wound healing assay was used to evaluate cell migration; E: Using the transwell assay, the cellular invasion was assessed. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs sh-NC group. CFI: Complement factor I; EdU: 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine.
- Citation: Du YJ, Jiang Y, Hou YM, Shi YB. Complement factor I knockdown inhibits colon cancer development by affecting Wnt/β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway and glycolysis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2646-2662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2646.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2646