Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2024; 16(6): 2404-2418
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2404
Published online Jun 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2404
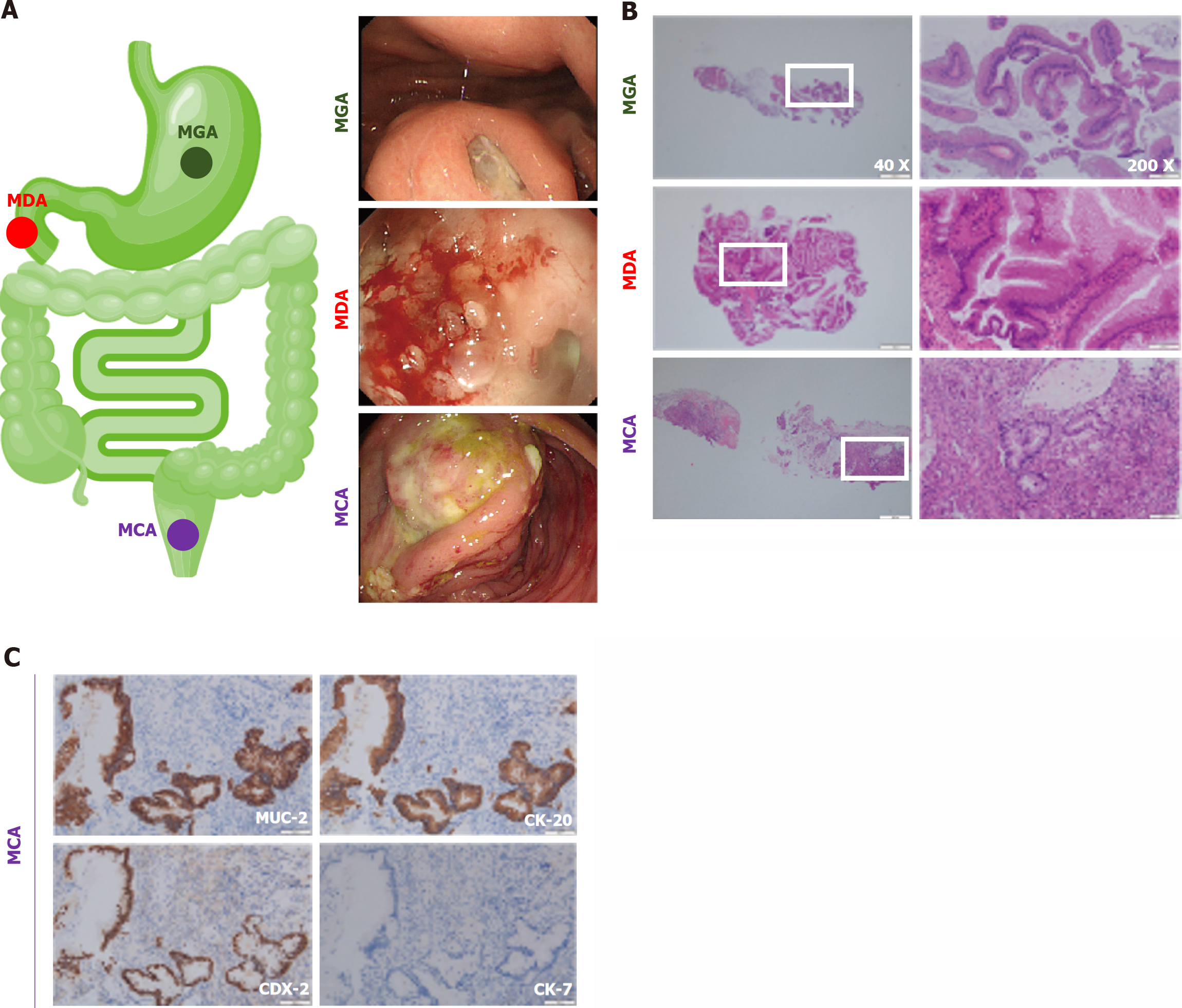
Figure 1 The endoscopic, hematoxylin-eosin staining, and immunohistochemistry photos of gastrointestinal mucous adenocarcinoma.
A: The endoscopic photos of gastrointestinal mucous adenocarcinoma (GMA), including mucinous gastric adenocarcinoma (MGA), mucinous duodenal adenocarcinoma (MDA), and mucinous colorectal adenocarcinoma (MCA). MGA, ulcer lesions on the posterior wall of the gastric body, with white coating and jelly-like material on the surface. MDA, duodenal bulb ulcer bleeding with accumulation of transparent jelly-like material. MCA, the electronic colonoscope was inserted 90 cm through the anus. There was a raised lesion with a diameter of about 5 cm, and the surface was covered with yellow and white coating; B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of GMA; C: Immunohistochemistry results of MCA, MUC-2, CK-20, and CDX-2 were positive while CK-7 was negative. MGA: Mucinous gastric adenocarcinoma; MDA: Mucinous duodenal adenocarcinoma; MCA: Mucinous colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Citation: Song J, Yan XX, Zhang FL, Lei YY, Ke ZY, Li F, Zhang K, He YQ, Li W, Li C, Pan YM. Unveiling the secrets of gastrointestinal mucous adenocarcinoma survival after surgery with artificial intelligence: A population-based study. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(6): 2404-2418
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i6/2404.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2404