Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 2091-2112
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2091
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2091
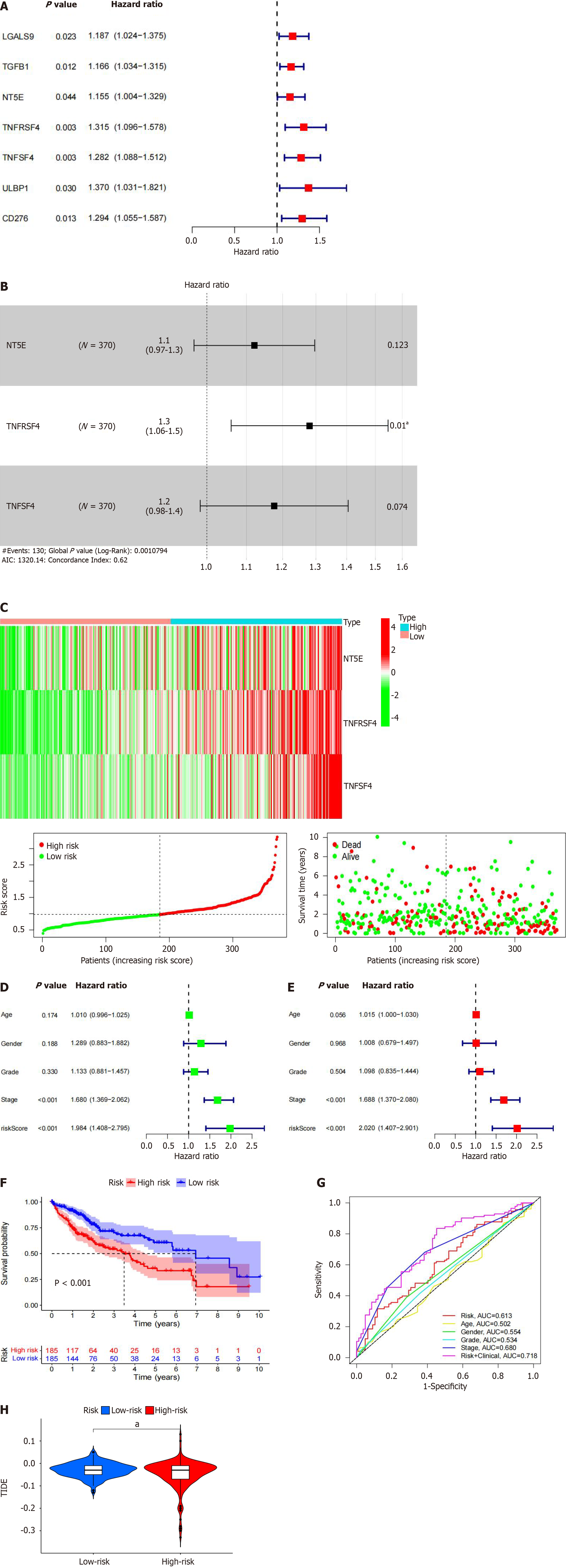
Figure 5 Risk model incorporating plexin domain-containing 1-associated immune checkpoints in hepatocellular carcinoma based on the The Cancer Genome Atlas database.
A: Construction of a prognostic immune checkpoint model associated with plexin domain-containing 1 (PLXDC1) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); B and C: Proportional regression model of Cox risk for PLXDC1 in HCC with associated immune checkpoints CD73, TNFRSF4, and TNFSF4; D and E: Univariate and multifactor Cox analysis of model risk scores combined with clinical factors; F: Prognostic analysis results; G: The accuracy of the Cox model risk prediction was assessed using receiver operational characteristic curves; H: The immune evasion ability and immunotherapy response were assessed in the high-risk and low-risk groups; the high-risk group had a better treatment outcome than the low-risk group. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. PLXDC1: Plexin domain-containing 1.
- Citation: Tang MY, Shen X, Yuan RS, Li HY, Li XW, Jing YM, Zhang Y, Shen HH, Wang ZS, Zhou L, Yang YC, Wen HX, Su F. Plexin domain-containing 1 may be a biomarker of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients, may mediate immune evasion. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 2091-2112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/2091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2091