Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 2038-2059
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2038
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2038
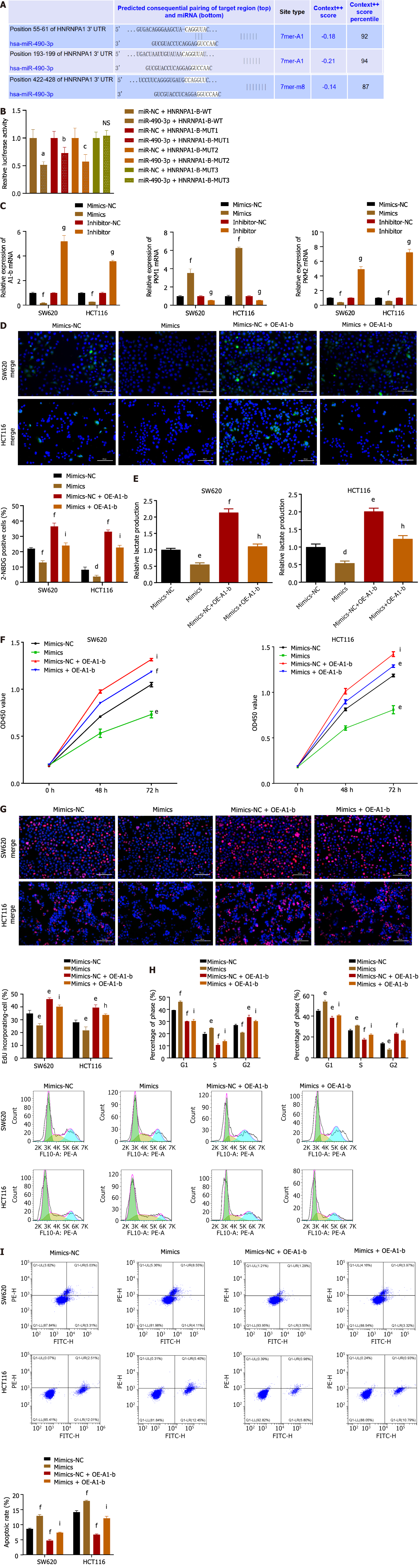
Figure 5 MiR-490-3p could target binding to heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein A1-b and inhibit the Warburg effect to attenuate colon cancer cell proliferation.
A: The binding sites of miR-490-3P and heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1) were predicted using TargetScan; B: The wild-type (WT) and mutant type (MUT) hnRNPA1-b 3’ untranslated region reporter plasmids were co-transfected with miR-490-3P control or mimics in HEK-293T cells; C: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis was performed to analyze hnRNPA1-b, PKM1 and PKM2 expression in SW620 and HCT116 cells transfected with miR-490-3P control or mimics or inhibitor; D and E: SW620 and HCT116 cells were transfected with miR-490-3P control or mimics or in combination of hnRNPA1-b overexpression plasmid for 48 h. Then glucose uptake and lactate production were evaluated. Scale bar: 100 μm; F: Cell viability of SW620 and HCT116 cells transfected with miR-490-3P control or mimic or conjugated with hnRNPA1-b overexpression plasmid for 72 h was detected by the cell counting kit-8 assay; G: 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine incorporation assays were performed using SW620 and HCT116 cells with miR-490-3P control or mimics or in combination with hnRNPA1-b overexpression plasmid. The percentage of proliferating cells (red fluorescence) to total cells (blue fluorescence) was calculated. Scale bar: 100 μm; H and I: Flow cytometry was performed to evaluate the effect of miR-490-3P control or mimics or in combination with hnRNPA1-b overexpression plasmid on the cell cycle distribution and apoptosis. aP < 0.001 vs miR-NC + HNRNPA1-B-WT; bP < 0.01 vs miR-NC + HNRNPA1-B-MUT1; cP < 0.01 vs miR-NC + HNRNPA1-B-MUT2; ns: P > 0.05 vs miR-NC + HNRNPA1-B-MUT3; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs mimics-NC; gP < 0.001 vs inhibitor-NC; hP < 0.01, iP < 0.001 vs mimics, n = 3. NC: Normal control; OE-A1-b: Overexpression of hnRNPA1-b.
- Citation: Wan XH, Jin GB, Yang Q, Hu JL, Liu ZL, Rao J, Wen C, Li PL, Yang XM, Huang B, Wang XZ. Novel miR-490-3p/hnRNPA1-b/PKM2 axis mediates the Warburg effect and proliferation of colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 2038-2059
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/2038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2038