Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 1890-1907
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1890
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1890
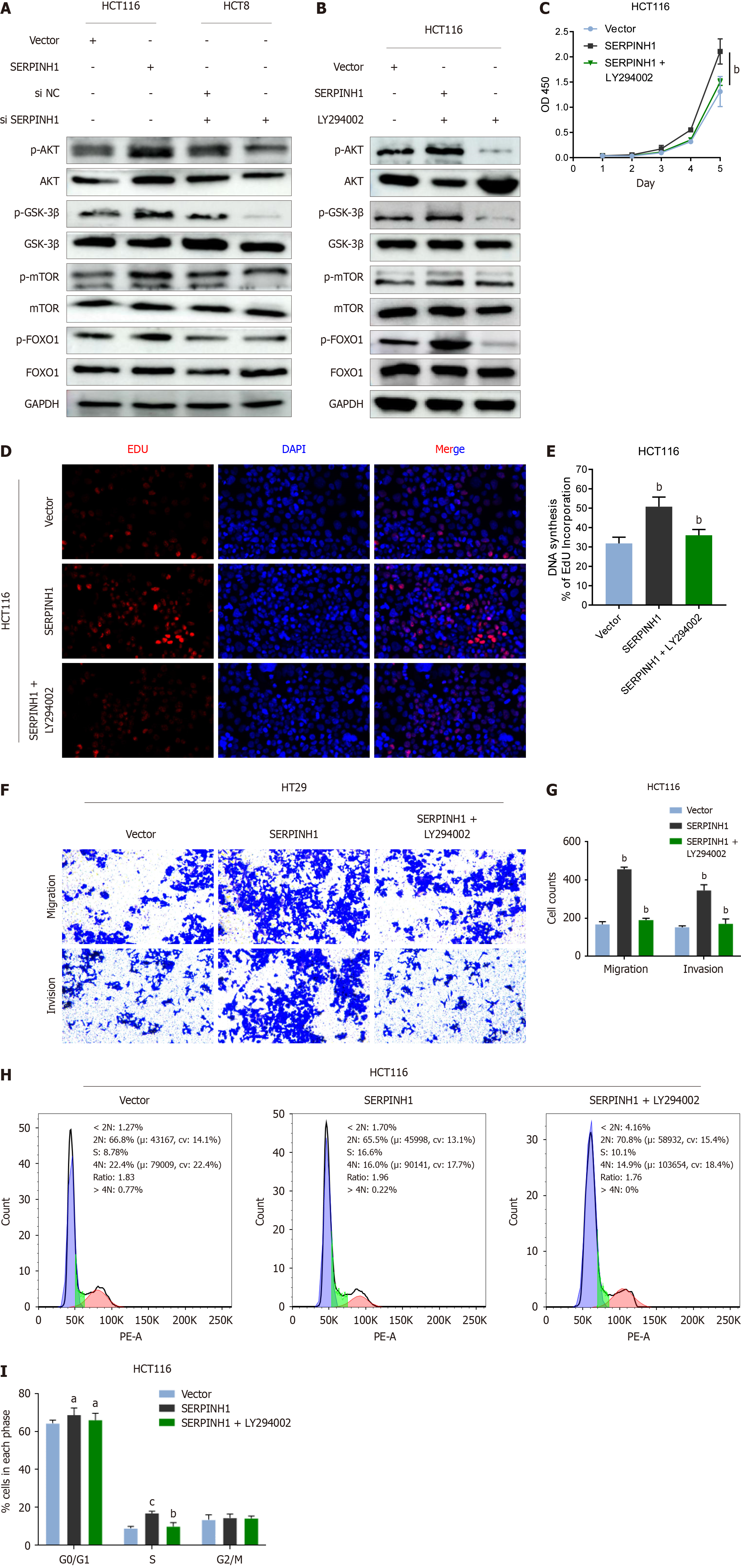
Figure 6 Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 promoted colorectal cancer progression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mechanistic target of rapamycin and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathways.
A: Western blotting analysis of p-AKT, total AKT, p-glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β, total GSK-3β, p-mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), total mTOR, p-FOXO1, and total FOXO1 in serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1 (SERPINH1)-overexpressed cells or SERPINH1 siRNA-infected cells; B: HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were treated with the AKT inhibitor LY294002 (20IM) and DMSO for 24 h, then harvested to examine the expression levels of the indicated proteins by western blotting; C-E: The proliferation ability of HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were determined by cell counting kit 8 assay and 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine assay; F and G: The invasive and migratory abilities of HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were determined by transwell assays after treatment with rapamycin and DMSO; H and I: The G0/G1 ratio of HCT116/SERPINH1 cells were determined by flow assays after treatment with rapamycin and DMSO. All the data are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. SERPINH1: Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade H member 1.
- Citation: Jin XS, Chen LX, Ji TT, Li RZ. SERPINH1 promoted the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 1890-1907
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/1890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1890