Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 1690-1704
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1690
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1690
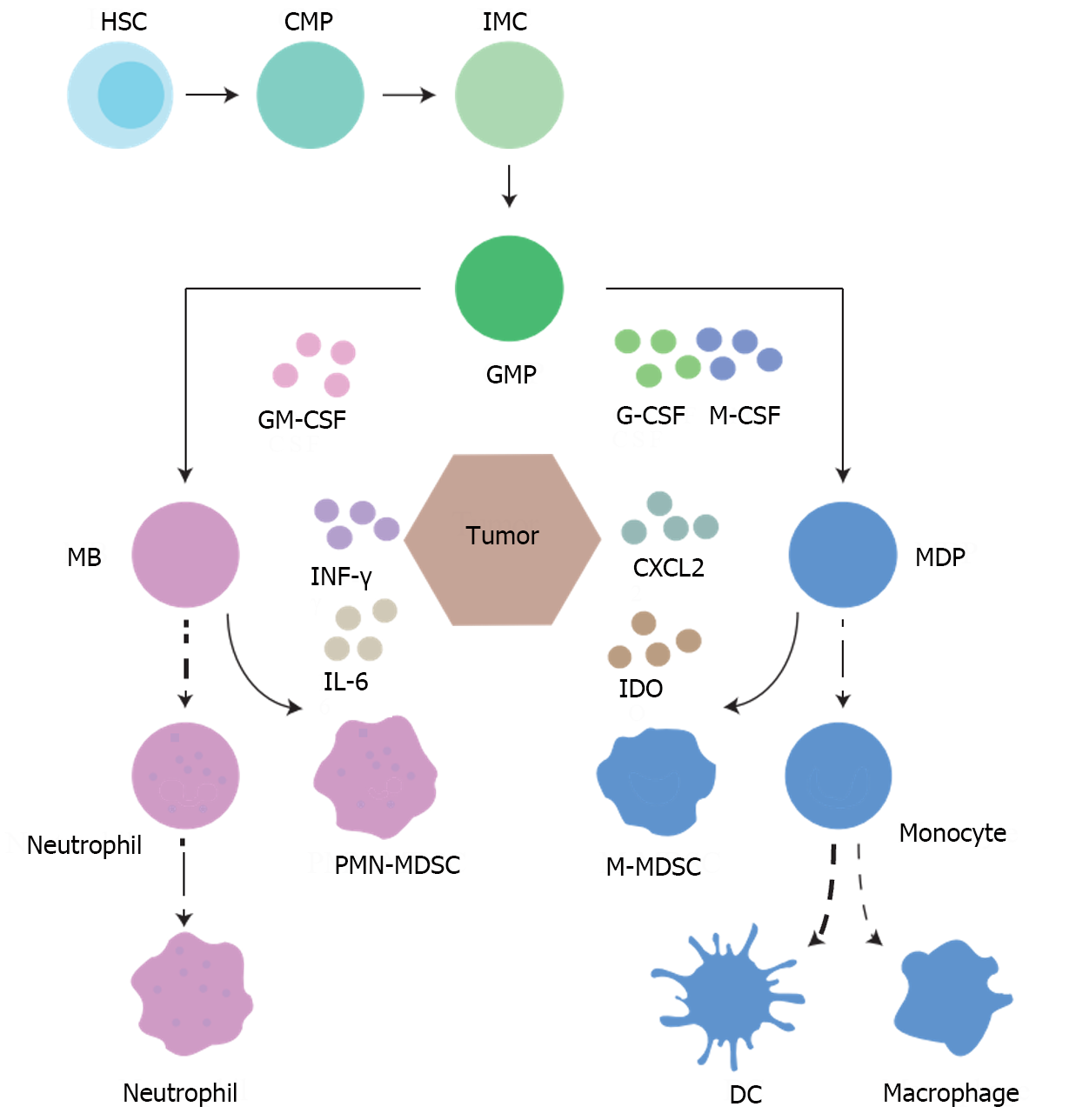
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of myeloid-derived suppressor cell development and differentiation.
Hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow differentiate into common myeloid progenitors (CMP) and then undergo CMP, myeloblast, and monocyte-dendritic cell progenitor processes that culminate in differentiation into monocytes or neutrophils. However, in patients with tumors, continuous stimulation often leads to defective differentiation of immature myeloid cells, which eventually differentiate into myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) with immunosuppressive properties. MDSCs are classified into two subsets: Monocytic MDSC and granulocytic polymorphonuclear MDSC. HSC: Hematopoietic stem cells; CMP: Common myeloid progenitors; GMP: Granulocyte-macrophage progenitor; MB: Myeloblast; MDP: Monocyte-dendritic cell progenitor; IMC: Immature myeloid cell.
- Citation: Nie SC, Jing YH, Lu L, Ren SS, Ji G, Xu HC. Mechanisms of myeloid-derived suppressor cell-mediated immunosuppression in colorectal cancer and related therapies. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 1690-1704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/1690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1690