Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 1676-1682
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1676
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1676
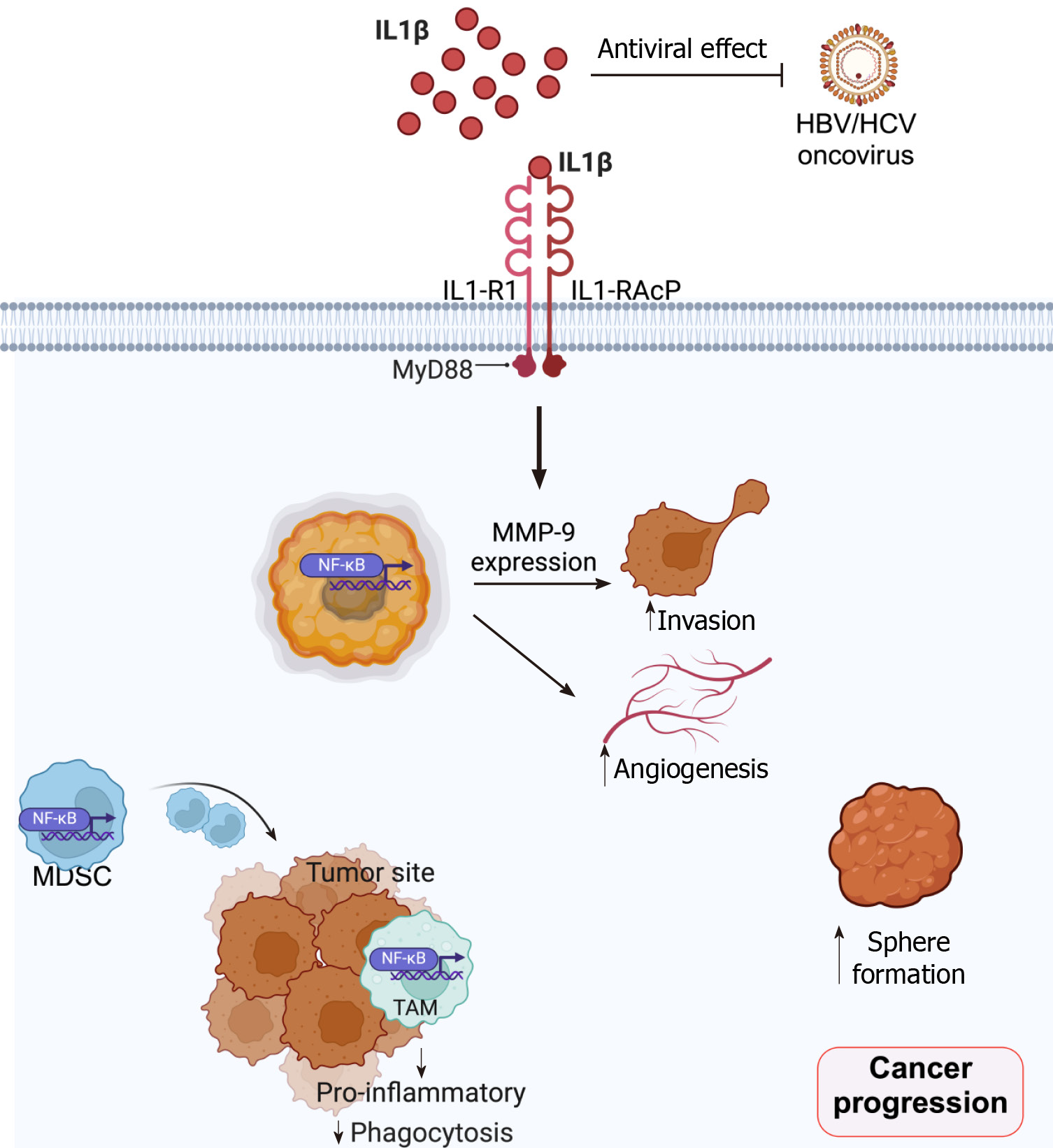
Figure 1 Schematic summary of roles of interleukin-1β in cancer progression.
Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) has an anti-hepatitis B virus/hepatitis C virus effect, which leads to a reduced risk of liver cancer. In contrast, IL-1β activates the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) signaling pathway in both cancer cells and immune cells, including myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAM). NF-κB activation in cancer cells triggers matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression and promotes invasion, angiogenesis as well as sphere formation. Activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in MDSC increases MDSC migration and infiltration to the tumor site, which further inhibits effector immune cells and promotes cancer progression. Moreover, NF-κB induction reduces the phagocytotic activity of TAM in the tumor site (Created by BioRender). IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase 9; Myd88: Myeloid differentiation primary response 88.
- Citation: Khawkhiaw K, Panaampon J, Imemkamon T, Saengboonmee C. Interleukin-1β: Friend or foe for gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 1676-1682
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/1676.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1676