Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1564-1577
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1564
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1564
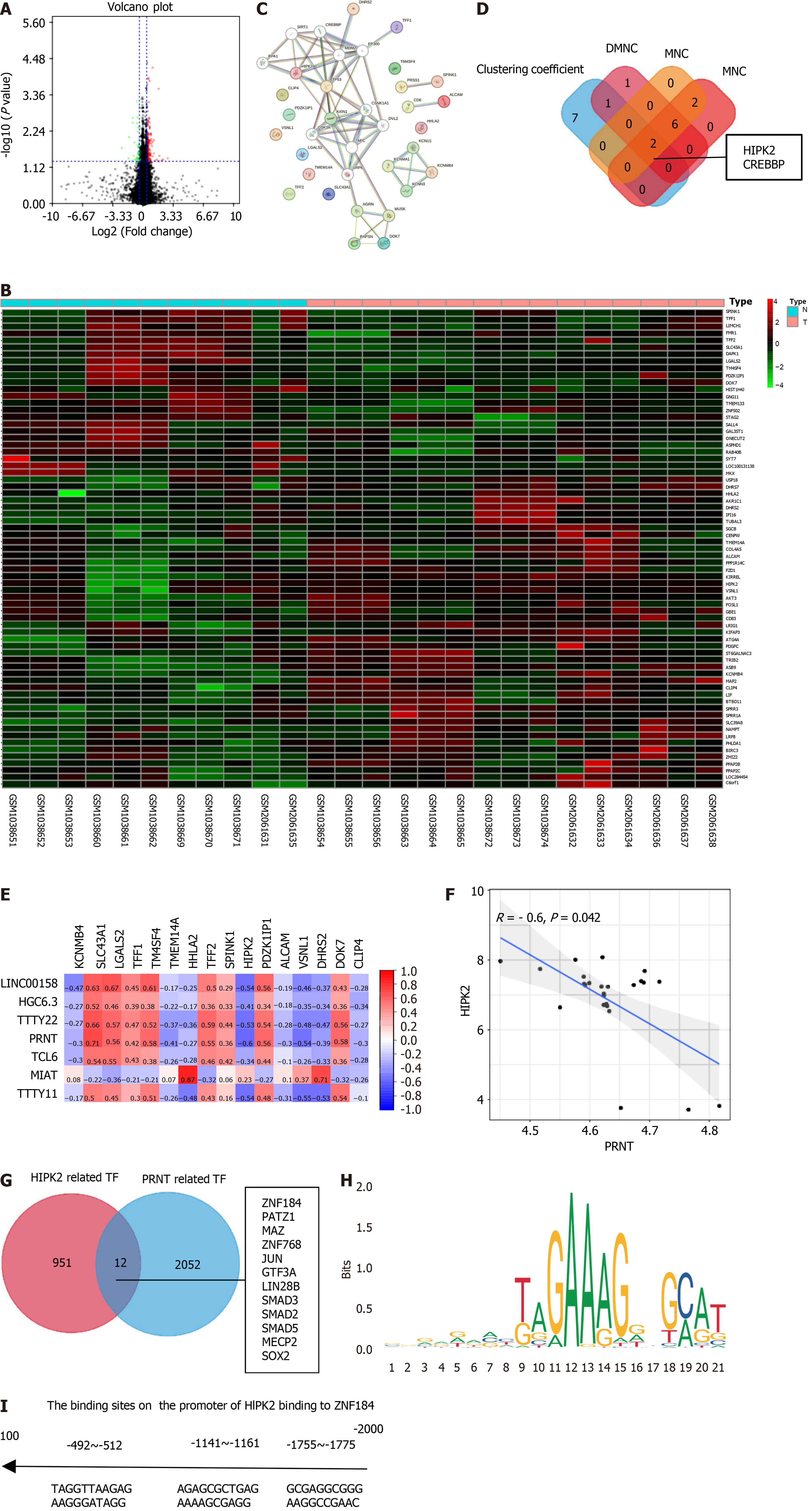
Figure 1 Differential expression analysis of oxaliplatin resistance-related genes in the Gene Expression Omnibus database.
A: Volcano plot of the oxaliplatin resistance-related genes showing differential expression between oxaliplatin-sensitive and oxaliplatin-resistant groups; B: Heatmap of oxaliplatin resistance-related genes; C: Protein-protein interaction of oxaliplatin resistance-related genes; D: Hub genes of the oxaliplatin resistance-related genes; E: Heatmap of the correlation between oxaliplatin resistance-related genes and long noncoding RNAs; F: Scatter plot of the correlation between prion protein testis specific (PRNT) and homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2); G: Venn plot of PRNT-related TFs and HIPK2-related TFs; H: Canonical ZNF184 binding motif via Joint Analysis of the Structural Parameters of Analytical Regulation (JASPAR); I: The binding sites of HIPK2 and ZNF184 predicted via JASPAR. PRNT: Prion protein testis specific; ZNF184: Zinc finger protein 184; HIPK2: Homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2.
- Citation: Li SN, Yang S, Wang HQ, Hui TL, Cheng M, Zhang X, Li BK, Wang GY. Upregulated lncRNA PRNT promotes progression and oxaliplatin resistance of colorectal cancer cells by regulating HIPK2 transcription. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1564-1577
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1564