Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2024; 16(3): 1029-1045
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.1029
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.1029
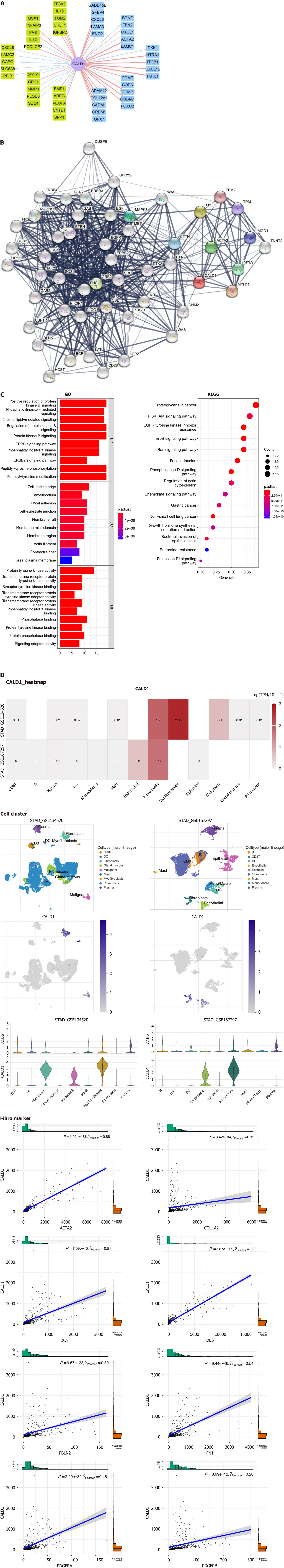
Figure 3 CALD1 gene is associated with PI3K-Akt-mTOR and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways in gastric cancer: Insights from bioinformatics and protein interaction studies.
A: Bioinformatics results showed that the CALD1 gene was significantly associated with the expression of members in the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway as well as the epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling pathway in gastric cancer; B: PPI network analysis of CALD1 showed that it interacts with a variety of proteins; C: GO and KEGG enrichment analyses showed that CALD1 was closely associated with the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; D: In-depth analysis revealed that CALD1 was highly expressed in fibroblasts and was significantly positively correlated with the expression of fibroblast surface molecules.
- Citation: Ma WQ, Miao MC, Ding PA, Tan BB, Liu WB, Guo S, Er LM, Zhang ZD, Zhao Q. CALD1 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in gastric cancer cells by modulating the PI3K-Akt pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(3): 1029-1045
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i3/1029.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.1029