Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2024; 16(3): 1029-1045
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.1029
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.1029
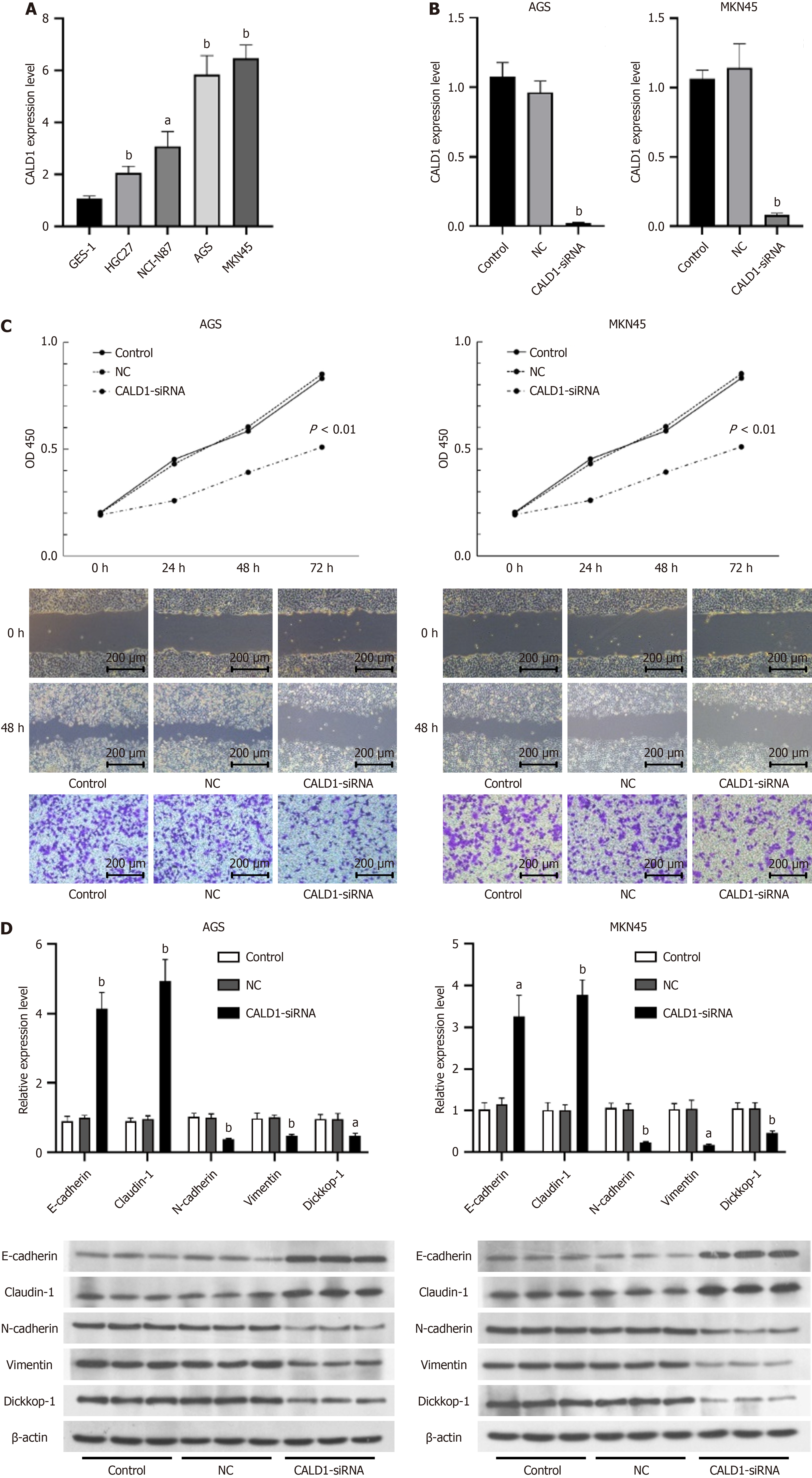
Figure 2 Inhibition of CALD1 in gastric cancer cell lines reduces cell activity, migration, and invasion, and alters epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker expression.
A: CALD1 expression levels were higher in gastric cancer cell lines HGC27, NCI-N87, AGS, and MKN45 than in gastric epithelial cell line GES-1, with the strongest expression found in AGS and MKN45 cells; B: The inhibitory effect of CALD1-siRNA was verified; C: After transfection of AGS and MKN45 cells with CALD1-siRNA, cell activity was significantly reduced, and the migration and invasion ability was decreased; D: The expression of E-cadherin and Claudin-1 was increased in AGS and MKN45 cells after inhibiting the expression of CALD1, while the expression of N-cadherin, Vimentin, and Dickkop-1 mRNA and protein was decreased. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Ma WQ, Miao MC, Ding PA, Tan BB, Liu WB, Guo S, Er LM, Zhang ZD, Zhao Q. CALD1 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in gastric cancer cells by modulating the PI3K-Akt pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(3): 1029-1045
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i3/1029.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.1029