Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2024; 16(10): 4264-4273
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4264
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4264
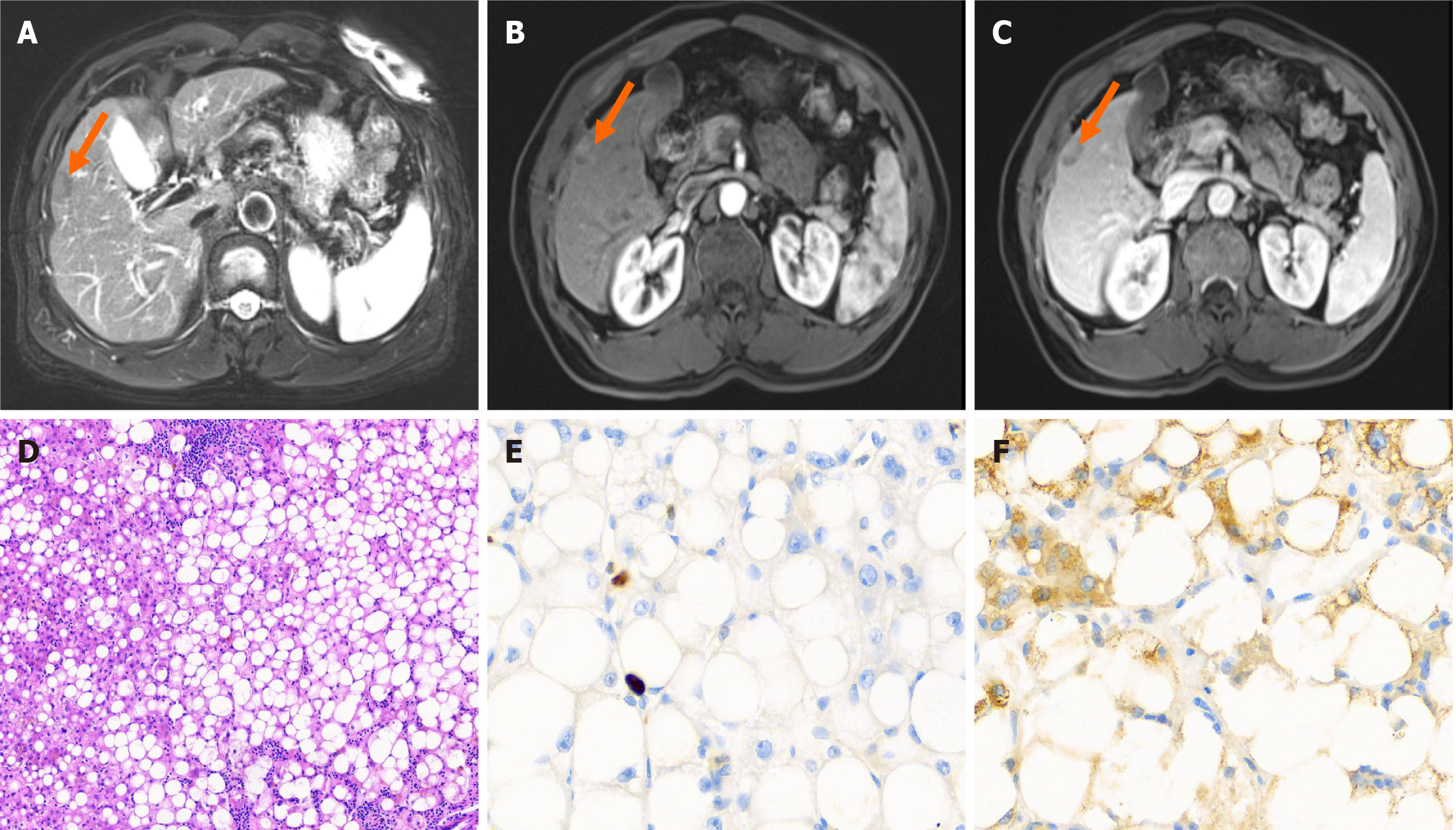
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging, pathological examination and immunohistochemical results of focal hepatic steatosis.
A: The lesion in segment S5 is slightly hypointense on the T2-weighted fat-suppressed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequence (arrow); B: The lesion begins to enhance during the arterial phase of MRI (arrow); C: The lesion shows less enhancement in the delayed phase of MRI compared to the adjacent liver parenchyma (arrow); D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining 100 ×; E: Ki-67 (positive, < 5%), immunohistochemical staining 400 ×; F: Hepatocyte (+), immunohistochemical staining 400 ×.
- Citation: Zhao Y, Bie YK, Zhang GY, Feng YB, Wang F. Rare and lacking typical clinical symptoms of liver tumors: Four case reports. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(10): 4264-4273
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i10/4264.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4264