Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2024; 16(10): 4264-4273
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4264
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4264
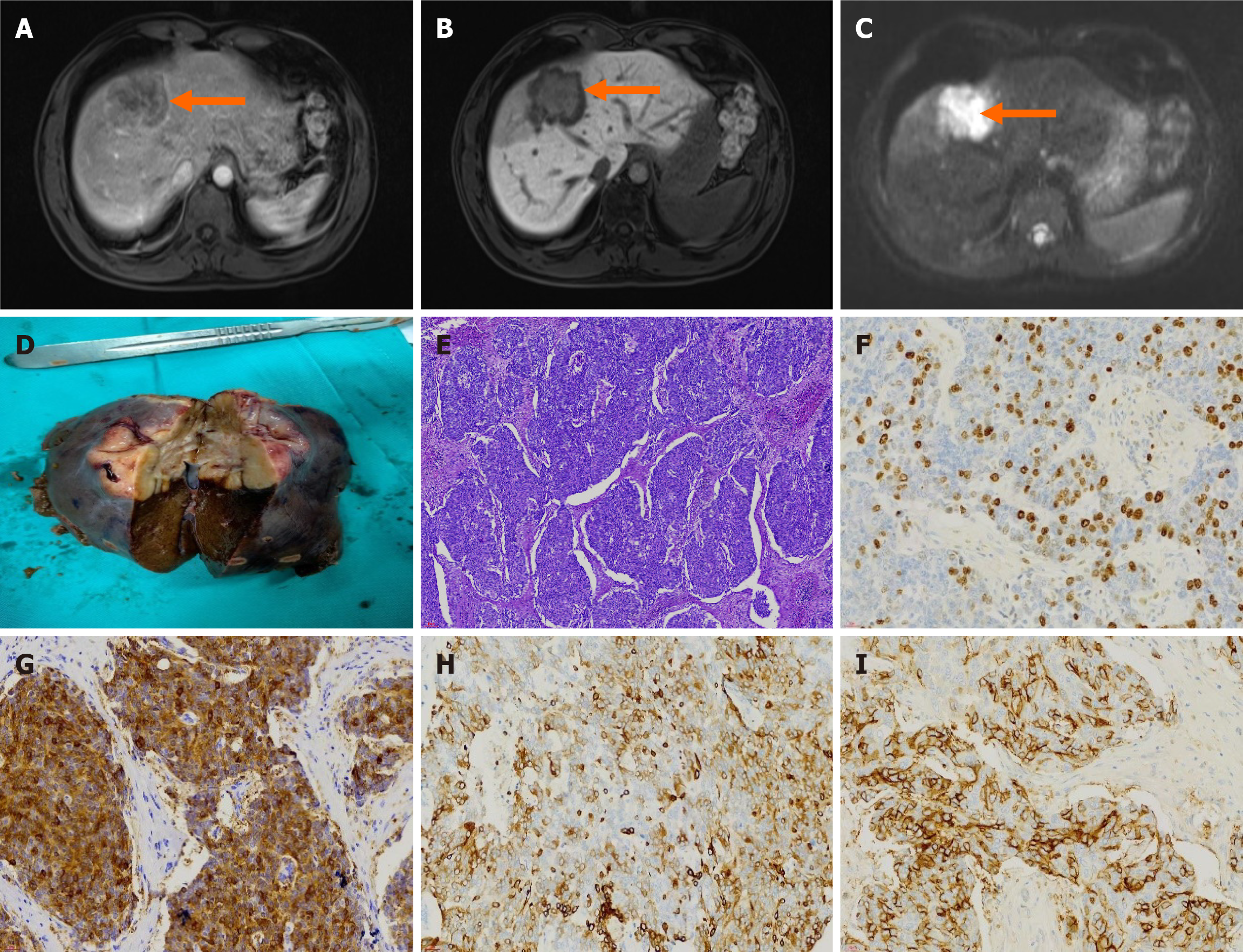
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging, pathological examination, and immunohistochemical results of primary hepatic neuroendocrine tumors.
A: The margins of the lesion showed enhancement during the arterial phase of magnetic resonance imaging, with the middle lobe exhibiting a mild septal-like enhancement pattern (arrow); B: The lesion in the hepatobiliary phase exhibited a low and slightly low signal (arrow); C: Diffusion weighted imaging revealed a high signal shadow of the lesion (arrow); D: Tumor pathology specimen; E: Hematoxylin and eosin staining 100 ×; F: Ki-67 positivity rate of approximately 30%, immunohistochemical staining 400 ×; G: synaptophysin cell positivity, immunohistochemical staining 400 ×; H: Cytokeratin wide cell positive, immunohistochemical staining 400 ×; I: CD56 partially cell positive, immunohistochemical staining 400 ×.
- Citation: Zhao Y, Bie YK, Zhang GY, Feng YB, Wang F. Rare and lacking typical clinical symptoms of liver tumors: Four case reports. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(10): 4264-4273
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i10/4264.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4264