Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2024; 16(10): 4115-4128
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4115
Published online Oct 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4115
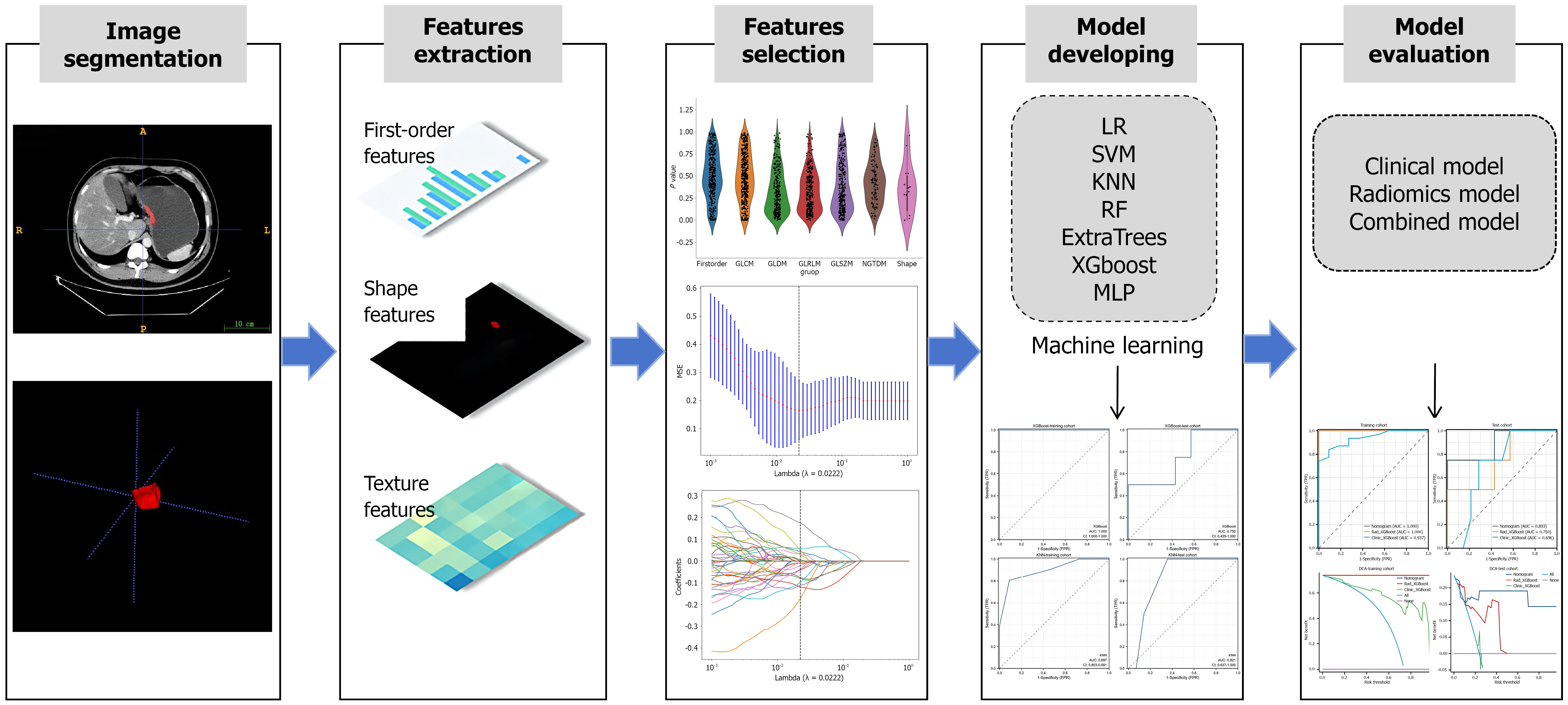
Figure 2 A flow chart of the radiomic analysis.
According to the computed tomography images, important imaging features were screened and combined with important clinical risk factors to generate a radiomic nomogram. The performance and clinical utility of the radiomic model in predicting the response of patients with advanced gastric cancer to neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy were evaluated through receiver operating characteristic curve analysis and decision curve analysis. LR: Logistic regression; KNN: K-nearest neighbor classification; RF: Random forest; XGBoost: EXtreme gradient boosting; MLP: Multilayer perceptron; SVM: Support vector machine; MSE: Mean squared error; TPR: True positive rate; FPR: False positive rate; DCA: Decision curve analysis.
- Citation: Zhang J, Wang Q, Guo TH, Gao W, Yu YM, Wang RF, Yu HL, Chen JJ, Sun LL, Zhang BY, Wang HJ. Computed tomography-based radiomic model for the prediction of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy response in patients with advanced gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(10): 4115-4128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i10/4115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4115