Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2023; 15(9): 1567-1594
Published online Sep 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1567
Published online Sep 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1567
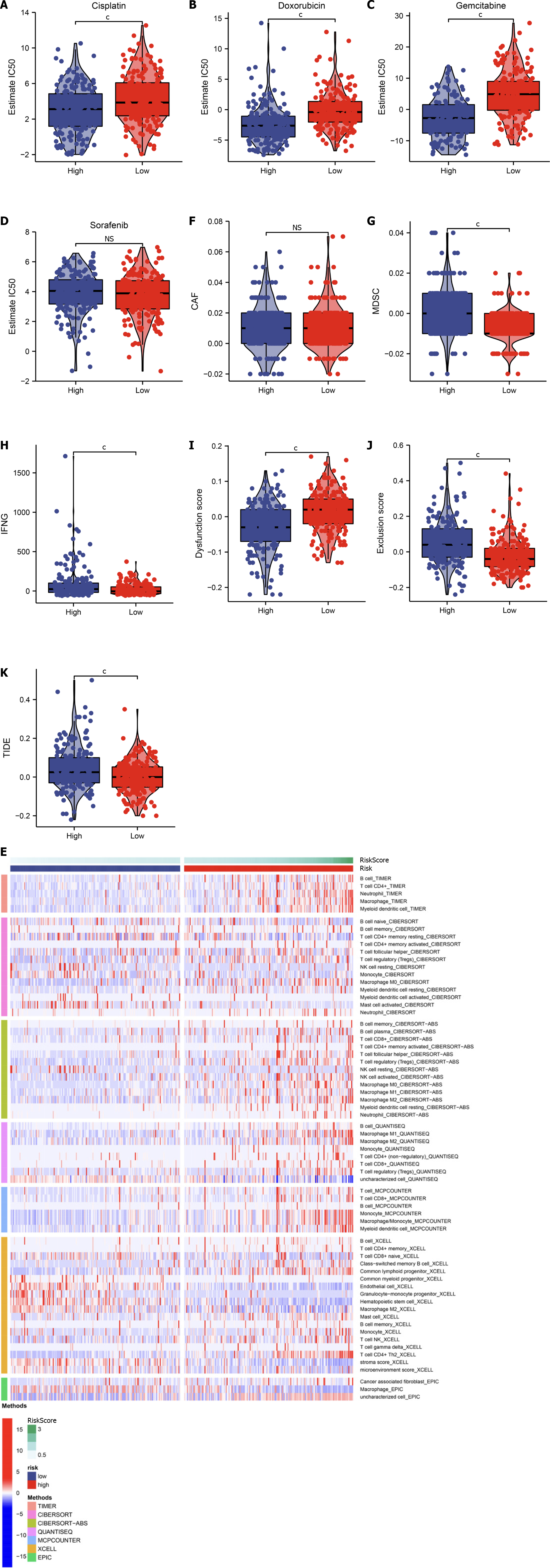
Figure 8 Assessment of the cellular senescence-relevant gene signature in predicting efficacy of pharmacological interventions in TCGA-LIHC dataset.
A–D: IC50 value of cisplatin, doxorubicin, gemcitabine, and sorafenib in low- and high-RiskScore hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs); E: Abundance of the tumor microenvironment components inferred by multiple algorithms; F–K: Comparison of carcinoma-associated fibroblast (CAF), myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC), interferon gamma (IFNG), dysfunction score, exclusion score and Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion levels in low- and high-RiskScore HCCs. cP < 0.001. ns: No significant difference.
- Citation: Wang HH, Chen WL, Cui YY, Gong HH, Li H. Cellular senescence throws new insights into patient classification and pharmacological interventions for clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(9): 1567-1594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i9/1567.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1567