Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2023; 15(8): 1366-1383
Published online Aug 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i8.1366
Published online Aug 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i8.1366
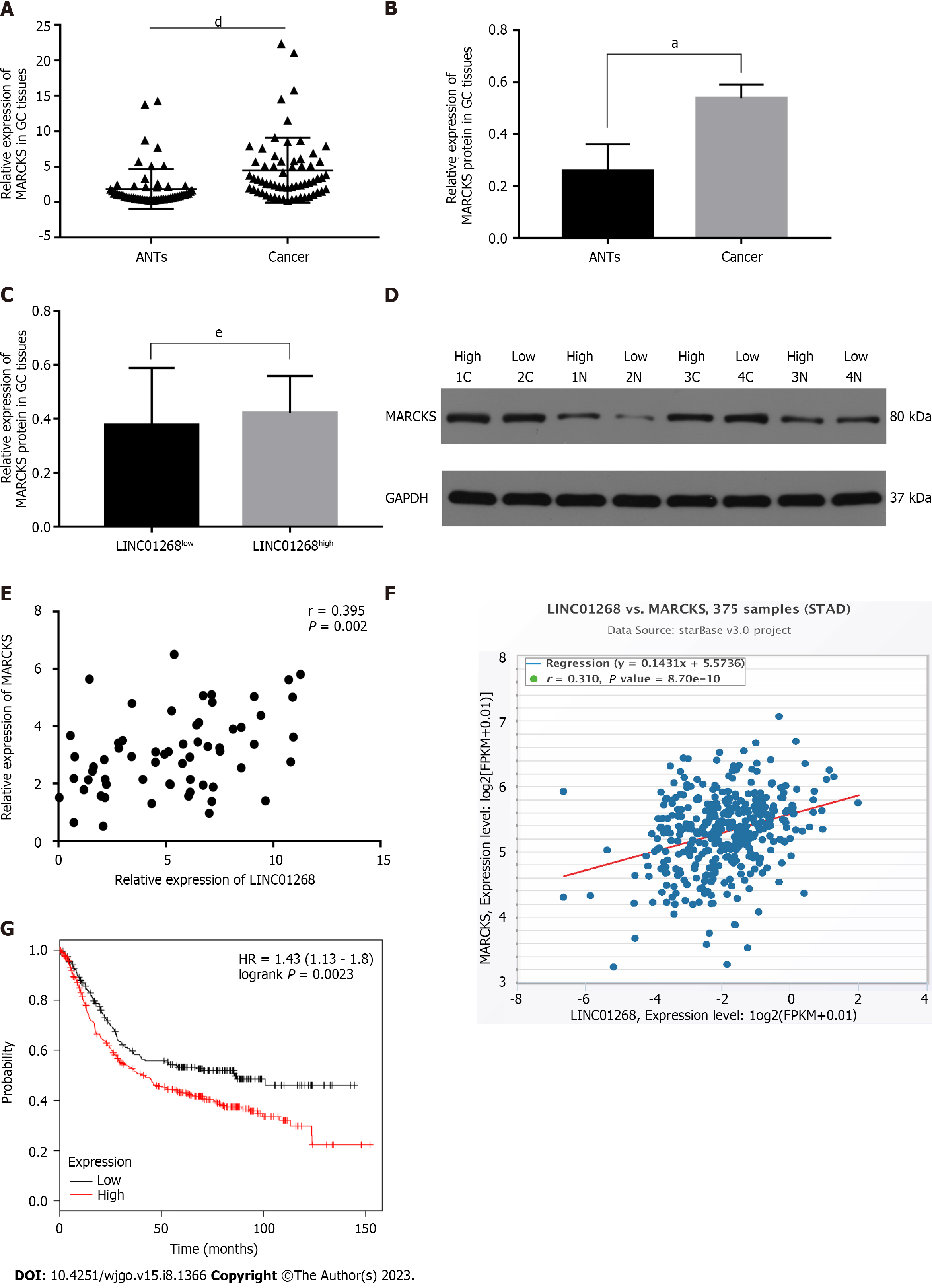
Figure 4 The expression level of myristoylated alanine rich protein kinase C substrate in gastric cancer and its relationship with LINC01268.
A: The relative mRNA expression level of myristoylated alanine rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS) in 62 cases of gastric cancer (GC) tissues was significantly higher than that of paired adjacent noncancerous tissue (ANTs). Expression levels were normalized to the ACTB levels. The results were shown as the mean ± SD; B: The protein levels of MARCKS in 4 pairs of GC tissues were significantly higher than those in paired ANTs. Expression levels were normalized to GAPDH levels. The results were shown as the mean ± SD; C: The protein levels of MARCKS in LINC01268 high expression groups were not higher than those in the LINC01268 low expression groups; D: Western blot detected the MARCKS protein expression of 4 pairs of GC tissues (C) and ANTs (N); E: The mRNA expression levels of MARCKS and LINC01268 in 62 cases of GC were positively correlated (r = 0.395, P = 0.002); F: LINC01268 and MARCKS showed a positive correlation in 375 GC samples in the starBase online database (r = 0.310, P < 0.0001); G: In Kaplan-Meier plotter online database, the prognosis and survival of 392 GC patients with high expression of MARCKS were worse than 239 GC patients with relatively low expression of MARCKS (log-rank P = 0.0023). aP < 0.05, dP < 0.0001, eP > 0.05. MARCKS: Myristoylated alanine rich protein kinase C substrate; GC: Gastric cancer; ANT: Adjacent noncancerous tissue; HR: Hazard ratio.
- Citation: Tang LH, Ye PC, Yao L, Luo YJ, Tan W, Xiang WP, Liu ZL, Tan L, Xiao JW. LINC01268 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and targeting MARCKS. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(8): 1366-1383
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i8/1366.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i8.1366